File - Ciencias esmeralda
advertisement
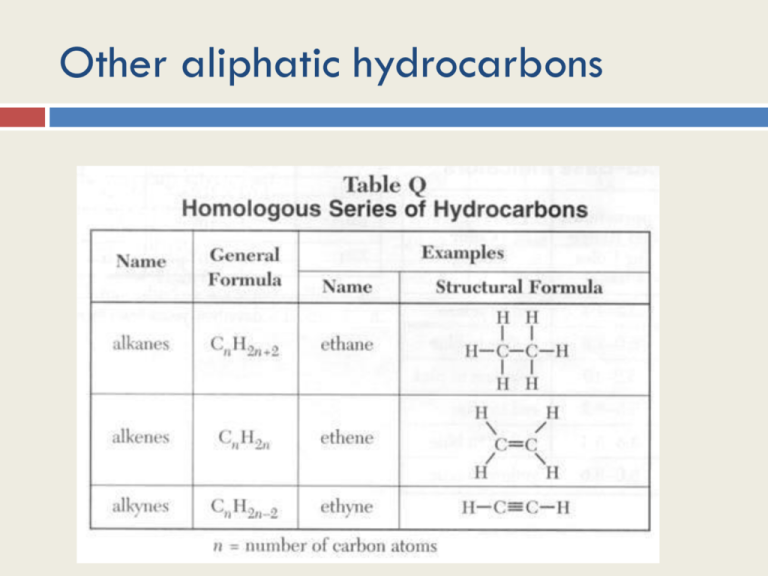
Other aliphatic hydrocarbons Objectives 1. To learn about naming and the structures of alkenes and alkynes and their branched chain isomers 2. To understand the effect of unsaturated bonds 3. To introduce the concept of cis and trans isomers; 4. To compare properties of saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons. Rules Alkanes have all single C-C bonds Alkenes have at least 1 C=C bond Alkynes have at least 1 CΞC bond Names all follow same pattern although some other common names exist to confuse you. Stick to format you’ve learnt! Names of alkenes and alkynes include numbers to indicate position of double and treble CC bonds! Unsaturated The double and triple bonds in alkenes and alkynes lead to them being referred to as unsaturated. These bonds can broken to allow the substitution in of other chemicals such as halogens These bonds can be broken to allow polymerisation. Polythene is made from long chains of ethene molecules joined by the breaking of their double bonds Polypropylene is made from joining propene molecules Alkenes I certainly learnt to call ethylene ethene and propylene propene (see slide 1) Molecular formula Alkanes CnH2n+2 Alkenes CnH2n Alkynes? What are the formulae of Pentane Hexene Octene Nonane isomers There are no isomers of ethene and propene Butene has 4 isomers Two of them have different spatial arrangements of their isomers and as such are called stereoisomers: They are named cis and trans which indicate whether subsituents are on the same or opposite sides of the double bond respectively. Becomes very important much later on with fats! Alkenes Cis and trans isomers Trans isomers are slightly more stable than cis isomers so have slightly lower heats of hydrogenation (a measure of how much energy they give out) Rules for naming Alkenes and Alkynes 1. Name the longest carbon chain that contains the double or triple bond 2. Number the longest chain from the end nearest the triple or double bond 3. Indicate the position of the double or triple bond with the number of the first unsaturated carbon. 4.Give the location and name of each substituent (alphabetical order) as a prefix to the alkene/alkyne name. Alkynes Note: I would call acetylene ethyne Alkynes Cycloalkenes These too exist. Again BPs and MPs are lower than for straight chain isomers They are also more stable Nomenclature is as for alkanes. When adding a side branch number carbons from the first side branch anticlockwise 1-methyl cyclohexene Plenary: Draw molecular models for 2-Butene 3-hexyne Write the formula for each in C H format Workout the molecular formula for alkynes Give the possible structure of the most stable C6H12 Alkene