Topic: Alkenes & Alkynes (unsaturated hydrocarbons)
advertisement

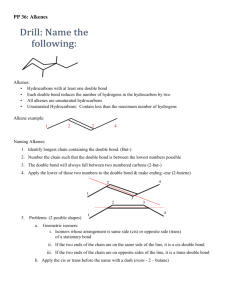
Topic: Alkenes & Alkynes (unsaturated hydrocarbons) Do Now: Name the following. Are the Isomers? Unsaturated hydrocarbons: organic compounds containing one or more double or triple bonds – can add more H by breaking the bond Alkenes • Another homologous series of hydrocarbons • Each member contains at least one double covalent bond between C atoms So alkenes are unsaturated • General formula = CnH2n Naming Alkenes 1. Count longest carbon chain. Note, it must contain the double bond – prefix tells # of C’s in longest chain and add ‘ene’ 1st member is C2H4: ethene H H C=C H H 3. If more than 4 Carbons – give 1st carbon in double bond the lowest possible number when numbering the chain ] 1-butene 2-butene If 2 double bonds = diene 1 2 3 4 1,3 pentadiene 5 Naming Branched-Chain Alkenes • 1st carbon in Double bond gets lowest number • Then name branches based on numbers assigned • Branch name and number come first when naming • Chain + ene come at the end – Example: 2-methyl 3-Nonene 3 methyl, 1-butene 4 2 1 3 Alkynes • • Homologous series of unsaturated hydrocarbons Each member contains at least one C≡C bond • General formula = CnH2n-2 Naming Alkynes • Same as alkene just add ‘yne’ to the end instead Structural molecular H–CC–H C2H2 H H–CC–C–H H C3H4 HH H–CC–C–C–H H H C4H6 H H H–C–CC–C–H H H C4H6 name ethyne Condensed Structural CHCH propyne CHCCH3 1-butyne CHCCH2CH3 2-butyne CH3CCCH3