Organic Review
advertisement

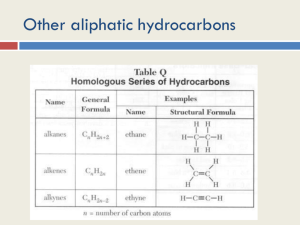
Organic Chem Review Sheet Part 1 Organic compounds have carbon atoms Can share one, two, or three pairs of electrons Organic compounds are molecular (covalently bonded) Carbon bonds form a tetrahedral shape Boiling point goes up as molecule gets bigger (greater intermolecular attraction) Isomers have the same molecular formula but different structural formula Butane has 2 isomers Pentane has 3 As number of carbon atoms in chain increase number of isomers increase Hydrocarbons contain only hydrogen and carbon Homologous series differ only in number of carbons in chain Saturated compounds only single bonds (alkanes) Unsaturated compounds contain double or triple bonds (alkenes and alkynes) Prefixes listed in table P according to number of carbon atoms in molecule Alkanes – CnH2n + 2 all single bonds end in ane Alkenes – CnH2n contain double bond end in ene Alkynes – CnH2n – 2 contain triple bond end in yne Number preceeding alkenes and alkynes represents location of double or triple bond Alcohols contain at least one OH 1 OH monohydroxy 2 OH dihydroxy 3 OH trihydroxy Name by dropping e and adding ol. Number before alcohol represents carbon that OH is attached to 1,2 Ethanediol (ethylene glycol) - antifreeze - dihydroxy alcohol 1,2,3 Propanediol (glycerol or glycerin) – in fats – trihydroxy alcohol Aldehydes contain a carbonyl group (C=O) attached to the end carbon Methanal is formaldehyde. CHO Ketones contain a carbonyl group on a carbon not at the end of the chain Minimum carbons in ketone is 3. Pentanone and up require number to tell where the CO is attached. Propanone is Acetone