Chapter 7: Alkenes and Alkynes I CH 7-1 Introduction
advertisement

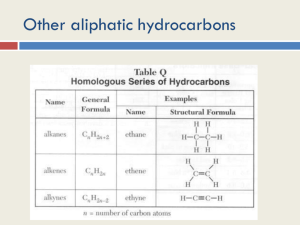
Chapter 7: Alkenes and Alkynes I CH 7-1 Introduction •Structure of alkenes & alkynes •Nomenclature •Relative stabilities of alkenes •Synthesis of alkenes via E1/E2 eliminations: E2 with small or bulky base Stereochemistry in E2 eliminations Cycloalkene eliminations Acid catalyzed alcohol dehydration •Rearrangements in SN1/E1 reactions •Alkene Hydrogenation (stereospecific syn addition of H2) •Terminal alkynes as nucleophiles Structure of Alkenes •“Un-saturated hydrocarbons” – contain C=C which is the key to understanding alkene chemical reactivity, HD = 2 • sp2 hybridization; trigonal planar; sigma and pi bonds •Each sp2 carbon has 3 sigma bonds & 1 pi bond. No C=C bond rotation due to the pi bond. s cis-2-butene p-orbitals “overlap” • Alkenes have Constitutional and Geometric isomers (cistrans). How many isomers exist for the formula: C4H8 Structure of Alkynes •“Un-saturated hydrocarbons” – contain C-C triple bond. • Linear geometry; sp hybridization; sigma and pi bonds H3C C C CH3 • Alkynes have Constitutional isomers (no geometric). How many isomers exist for the formula: C 4H 6 (Hint: nine isomers: 3 alkyne, 2 alkene, 4 ring)