Summary from Organic Chemistry Packet:
advertisement

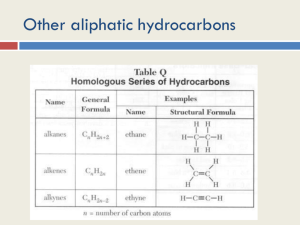
Summary from Organic Chemistry Packet: Introduction to organic chemistry 1. Nomenclature based on alkanes • Know alkanes for C1-C10 • Recognize the formula/name of – Alkenes (double bond) – Alkynes (triple bond) – Cycloalkanes (ring structure) Ex: Write the chemical formula and structural formula for: Octane 2- Butyne 1, 3- Heptadiene Hydrocarbons • Compounds of C and H and often a third or more additional elements • Subgroups: – Alkanes: Containing only C-C single bonds – Alkenes: C=C double bonds as well as single bonds – Alkynes: carbon-carbon triple bonds as well as single bonds. – Aromatic: hydrocarbons containing benzene rings. 2. Branched alkanes and isomers • Understand the basic rules for writing & naming branched alkanes. • Recognize and name structural isomers Ex: Name the following molecules: Hydrocarbons & Structural Isomerism Isomers of C5H12 CH 3CH2 CH2CH2 CH3 Pentane CH3 CH 3CHCH 2CH3 2-Methylbutane CH3 H3CCCH3 CH3 2,2-Dimethylpropane C5H12 has 3 structural isomers. C6H14 has 5 C7H14 has 9 And so on How many isomers can you draw for heptane? Alkenes: Compounds with C=C Double Bonds • Result of loss of free rotation about the C=C brings about “Geometric Isomers” • Increase in reactivity over alkanes • X-Y addition reactions are possible • X2, H2, HX and H2O can add across the double bond. Geometric (stereo) Isomers: • Recognize the terms cis-, trans- isomers – Unsaturated molecules – Orientation around the double bond Naming Alkenes: cis & trans Alkynes • Alkynes have carbon-carbon triple bonds. • C2H2: common name = acetylene systematic name = ethyne Preparation: CaC2(s) + 2H2O(l) C2H2 (g) + Ca(OH)2(s) Aromatic compounds • Benzene, C6H6, is a key molecule in chemistry. • It is the simplest aromatic compound, a class of compounds so named because they have significant, and usually not unpleasant, odors. Functional Groups: • Recognize functional groups • Name compounds based on functional groups Organic chemistry & reactions • Be familiar with some basic properties of an organic reaction: – – – – Combustion (know this for sure!) Condensation (H2O removed) Addition ( of a halogen to an unsaturated alkane) Substitution (of a halide)