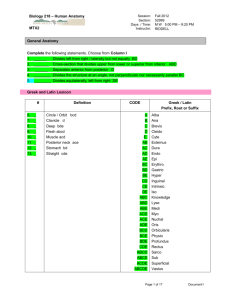
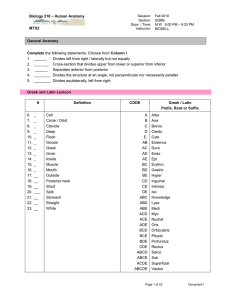
BIOL 218 F 2013 Practice MTX 2 Muscles Q 131011
advertisement

Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Practice Example Midterm Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL General Anatomy Complete the following statements. Choose from Column I ______ Divides left from right / laterally but not equally _______ Cross-section that divides upper from lower or superior from inferior ______ Separates anterior from posterior ________ Divides the structure at an angle, not perpendicular nor necessarily parallel ________ Divides equilaterally, left from right Greek and Latin Lexicon # _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ Definition Circle / Orbit Clavicle Deep Flesh Muscle Posterior neck Stomach Straight CODE Greek / Latin Prefix, Root or Suffix A B C D E. AB AC AD AE BC BD BE CD CE DE ABC ABD ABE ACD ACE ADE BCD BCE BDE CDE ABCD ABCE ACDE ABCDE Alba Ana Brevis Cleido Cyte Externus Dura Endo Epi Erythro Gastric Hyper Inguinal Intrinsic Iso Knowledge Lyse Medi Myo Nuchal Oris Orbicularis Physio Profundus Rectus Sarco Sub Superficial Vastus Page 1 of 17 Document1 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Practice Example Midterm Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Skeletal System / Articulations 1. Stability is an A. direct or B. indirect in relationship to probability of dislocation or injury. B Arrange the selection of joints per the following spectrum of relationships. Choose from Column III Most Mobile Least Mobile Least Stable Most Stable Page 2 of 17 Document1 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Practice Example Midterm Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL SKELETON Identify the indicated bones. See Column II for Choices Name this bone Name this bone Name this bone Name these bones Name these bones Name these bones Page 3 of 17 Document1 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Practice Example Midterm Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Fill In the term for the following definitions of muscular -skeletal movement. Choose from Column IV TERM Definition Increases the angle between articulating structures in a hinge joint and in the sagittal plane Movement of a bone or structure toward the midline, toward anatomical position Movement that turns the palmar surface posteriorly Movement of a bone or appendage away from the midline Circles in the air with your arms Fill In the term for the following definitions of muscular -skeletal movement. Choose from Column IV Primary contraction Opposing contraction Assisting and stabilizing contraction Complete the sentence by filling in the missing term. Choose from Column V Fibrous connective tissue that connects one bone to another _____. Nutrients are supplied to the chondrocytes of the articular cartilage by _____fluid. Your shoulder and other synovial joints have many moving parts that rub against one another. One of the structures that helps reduce friction between these parts is a fluid-filled sacs called: menisci tendons vesicles bursae Muscles Fill In the following table for muscle tissues. Choose from Column VI TERM Definition Connective tissue that covers muscle cells / muscle fibers Connective tissue that covers muscle fascicles Connective tissue that covers muscles Cell membrane that covers muscles cells Connective structure that is also named the parietal pericardium A motor neuron communicates with a skeletal muscle fiber by releasing ___ _____ into the synaptic cleft. Page 4 of 17 Document1 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Practice Example Midterm Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL List the muscles that belong to the following groups Rotator Cuff Quadriceps Hamstrings Identify the regional location for each of the muscles listed below. See COLUMN RIGHT for choices Muscle 2. 3. 4. 5. CODE Flexor Carpi Radialis Tibialis anterior Sternocleidomastoid Levator Scapulae A B C D E CHOICES Regional Location Cephalic and / or Cervical Posterior / Dorsal Vertebral Column / Acromial Anterior / Ventral / Abdominal / Pelvic Brachial Femoral, Sural, or Crural Fill in the following table for muscle structure and function. Mark A for True and B for False Attribute Cardiac Smooth Skeletal Voluntary Control Self rhythmic Can have agonist vs antagonist functions / relations Sarcomeres arranged end to end Identification Muscle Attribute Classification Mark A for True and B for False Muscle Origin Insertion Action Biceps brachii Quadriceps femoris Pectorails major Gastrocnemius Page 5 of 17 Document1 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Practice Example Midterm Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Match the Muscle to its correct anatomical region as illustrated. See COLUMN RIGHT for Muscle choices. Illustration of MUSCLE Compartments / Regions 6. 7. 8. 9. __Deep Anterior __Lateral __Posterior Is this perspective A. patient right or B. patient left CODE A B C D Page 6 of 17 MUSCLES Brachioradialis Extensor digitorum Flexor Carpi radialis Flexor Digitorum Profundus Document1 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Practice Example Midterm Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL ILLUSTRATION of MUSCLE SHAPES Referring to the illustration above, fill in the following 2 tables with the correct reference CODE.. Place the correct CODE next to each term. NAME CODE SHAPE Biceps brachii Bipennate Deltoid Circular Extensor digitorum Convergent Page 7 of 17 CODE Document1 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Practice Example Midterm Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL GENERAL MUSCLE CYTOLOGY STRUCTURE IDENTIFICATION 10. Identify the myofibrils ( 2 answers) 11. Identify the sarcolemma 12. Identify the myofilaments Page 8 of 17 Document1 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Practice Example Midterm Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL The portion of the skeletal muscle that attaches to a stationary bone is called the: A. insertion B. origin C. belly D. sarcomere All of the following flex the forearm synergistically except: A. biceps brachii B. brachialis C. triceps brachii D. brachioradialis One location for intramuscular injections is in the upper arm in this muscle that forms the rounded part of your shoulder. What muscle is that? A. subscapularis B. deltoid C. biceps brachii D. pectoralis major The portion of the skeletal muscle that attaches to a, or the most,SLV stationary bone is called the: A. insertion B. origin C. belly D. sarcomere Your biceps brachii works as a ______ class lever system. A. first B. second C. third D. fourth The _________ muscle's name means “chewer”. Its function is to elevate the mandible. A. masseter B. buccinator C. mentalis D. platysma Page 9 of 17 Document1 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Practice Example Midterm Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL 13. Which of these muscles is not located in the anterior thoracic region? A. pectoralis major B. serratus anterior C. pectoralis minor D. latissiumus dorsi All of the following flex the forearm except: A. biceps brachii B. brachialis C. triceps brachii D. brachioradialis Muscles on the anterior surface of the forearm act as: A. flexors of the hand B. extensors of the hand C. adductors of the forearm D. abductors of the forearm Which of the following muscles is not a flexor of the leg at the knee? A. vastus lateralis B. semimembranosus C. semitendinosus D. biceps femoris What is the antagonistic muscle to the gastrocnemius? A. fibularis longus B. soleus C. tibialis anterior D. rectus femoris Page 10 of 17 Document1 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Practice Example Midterm Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Referring to the illustration above, identify the indicated muscles from COLUMN VII and VIII Identify the position fof the patient choosing from the terms available in COLUMN I. Muscle 14. 15. 16. 17. Name this MUSCLE Name this MUSCLE Name this MUSCLE Name this MUSCLE 18. In WHICH POSITION is this patient ? Page 11 of 17 Document1 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Practice Example Midterm Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Page 12 of 17 Document1 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Practice Example Midterm Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL THIS PAGE LEFT PURPOSELY BLANK Page 13 of 17 Document1 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Practice Example Midterm Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL MULTIPLE CHOICE CODES CODE I PLANES / Perspectives A B C D E AB AC. AD AE BC BD BE CD CE DE ABC ABD ABE ACD ACE ADE BCD BCE CDE ABCD ABCE ABDE ACDE BCDE ABCDE Around-About Caudal Circumferential Coronal/Frontal Cranial Direct Inverse Left Medial Oblique Parasagittal Prone Reverse Right Sagittal Supine Transverse II BONES Carpals Clavicle Coccyx Costals Coxal Digits Ethmoid Femur Fibula Frontal Humerus Hyoid Ilium Incus Ischium Lacrimal Malleus Mandible Maxillae Metacarpal Metatarsals II BONES continued Occipital Palatine Patella Pubis Radius Sacrum Scapula Sphenoid Stapes Sternum Tarsal Temporal Tibia Ulna Vertebrae Cervical Vertebrae Lumbar Vertebrae Thoracic Zygomatic III COMMON JOINT Ankle Hip Knee Sacroiliac Shoulder Suture of Skull IV MOVEMENT Abduction Adduction Agonist Antagonist Circumduction Contraction Contraction Assisting Contraction Primary Contractiuon Opposing Depression Dorsiflexion Elevation Eversion Extension Flexion Hyperextension Hyperflexion Inversion Lateral flexion Plantar flexion Pronation Protraction Rotation Supination Synergist V JOINTS & SUTURES VI HISTOLOGY Amphiarthrotic Articular Ball and Socket Bursae Cancellous Cartilaginous Condyloid Diarthroses Fibrous Elbow Gomphosis Hinge Ligament Pivot Planar Phalanges Saddle Sliding / gliding Suture Symphyses Synarthrosis Synchondrosis Syndesmosis Synovial Tendon Vertebrae First Class Second class Third Class Pulley A Band Acetylcholine Actin Axon Endomysium Epicardium Epimysium Fascicle H Band I Band Myofilament Myocardium Myomysium Myosin Neuro-mus Junction Perimysium Rock Band Sarcolemma Sarcomere Sarcoplasm Sinoatrial node Synaptic cleft Tendon Terminal cisterni Tropomyosin Troponin Z Disc Page 15 of 17 Document1 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Practice Example Midterm Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL THIS PAGE LEFT PURPOSELY BLANK Page 16 of 17 Document1 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Practice Example Midterm Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL MULTIPLE CHOICE CODES CODE VII MUSCLES A B C D E AB AC AD AE BC BD BE CD CE DE ABC ABD ABE ACD ACE ADE BCD BCE BDE CDE ABCD ABCE ABDE ACDE BCDE ABCDE Abductor pollicis longus Adductor Longus Biceps Brachii Biceps Femoris Brachioradialis Deltoid Extensor Carpi Extensor carpi radialis longus Extensor Digitorum Extensor Digitorum Longus Extensor Retinaculum External Oblique Flexor Carpi Flexor carpi ulnaris Forearm Gastrocnemius Gluteus Maximus Infraspinatus Internal oblique Lattisimus Dorsi Levator scapulae Masseter VIII MUSCLES continued X MUSCLE FORM Orbicularis Oris Bipennate Orbucularis Oculii Circular Pectineus Convergent Pectoralis Major Parallel Pectoralis minor Unipennate Quadriceps Femoris Rectus Abdominis Rectus Femoris Sartorius Serratus Anterior Subscpaularis Supraspinatus Temporalis Teres major Teres minor Thigh Tibialis Anterior Transverse abdominis Transverse oblique Trapezius Triceps Brachii X1 BONE Structures Apex Condyle Fossa Inferior Edge / margin / border Lateral Edge / margin / border Lateral Epicondyle Linea aspera Mastoid process Medial Edge / margin / border Medial Epicondyle Ramus Spinous process / Spine Styloid process Superior Edge / margin / border Transverse Process Trochlea Vertebral Body anterior arm anterior leg anterior torso forearm posterior arm posterior leg posterior torso Page 17 of 17 Document1