PPTX
advertisement

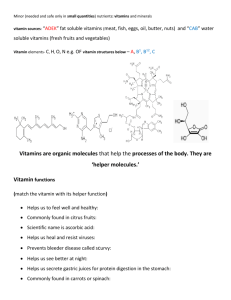
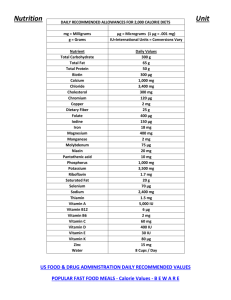
Huba Nasir Rowan University Students Essential Vs. Non-Essential Nutrients Essential Our bodies cannot make it so we have to get it from our diet to maintain optimal health Examples: carbohydrates fats Proteins some vitamins and minerals (Micronutrients) Non-Essential nutrient. Body can make the Carbohydrates √ √ √ √ √ All living cells contain carbs Primary energy source for nervous system Primary energy during high intensity exercise Protein Sparing effect Helps burn fat (Prevents Ketones) Sources of Carbs Lipids (Fats) • • • • Primary fuel at rest & light exercise Protection for organs Insulation Key component creating cell membranes • Transport fat soluble vitamins (A,D,E,K) • Hunger depressor Sources of Lipids Proteins Functions Enzymes speed chemical reactions Antibodies Transport molecules (HDL and LDL) Fluid and acid base balance Hormones Oxygen carriers (hemoglobin) Structural Proteins (building tissue: tendons, muscles, hair, other tissues) Micronutrients Vitamins a) Fat Soluble b) Water Soluble Minerals a) Major Minerals b) Trace Minerals Vitamin A Functions ♦ Immune defenses ♦ Vision ♦ Normal cell development ♦ Skin, bone and body growth(children) Vitamin D Benefits: • • • • • • Promotes cell growth Supports healthy immune system Promotes calcium absorption Prevention of depression Linked to weight loss Encourages good moods Vitamin E “anti-oxidant”-serves to defend against “oxidation” May help to prevent against heart disease May also be important in immune system Vitamin K Synthesis of proteins required for blood clotting & bone formation Half produced by bacteria in colon Deficiencies are rare Water Soluble Vitamins B Complex Thiamine (B1)- carb. Metabolism Riboflavin (B2)- Red Blood Cell Transformation B6- protein synthesis and neurotransmitters in brain B12- RBC formation, anemia Niacin- may help lower cholesterol Pantothenic acid (B5)-component of acetyl-CoA Folic acid (B8)- DNA & RNA synthesis Biotin-oxidation of fatty acids Folic acid, B6, B12- reduce CVD risk Vitamin C Also known as ascorbic acid Most widely consumed vitamin Anti-oxidant Helps vitamin E to function Synthesis of collagen Promotes immune function Enhances iron absorption Minerals Calcium : Found in bones, teeth, but also in cell Function: • Bone • Nerve transmission • Regulation of heartbeat • Muscle contraction Iron Functions: 1. Red Blood Cell Formation 2. CytochromesEnergy transfer in Electron Transport Chain 3. Immune System 4. Normal Brain Function Magnesium Facts: • Found in bone, muscle, heart • Assists enzymes to release energy • Improves insulin sensitivity Sodium Functions: • Maintains Fluid Balance • Maintains acid-base balance • Needed for muscle contraction & nerve transmission Potassium Maintain Fluid balance Proper functioning of the heart Zinc Functions: Enzymatic Reactions Involved in growth Immune system Affects “behavior & learning” Healthy Eating Tips Have Breakfast Eat Fruits and Vegetables Exercise Avoid empty calories (sat and trans fat) Drink Plenty of Water Prepare your own meal! smoking References https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/20140619085129-263590413-natural-sourcevitamin-e-market http://www.fightyourinfertility.com/1166/four-step-system-to-treat-high-prolactinand-low-progesterone-levels/4-zinc-rich-foods http://kidneysdisease.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/04/foods-containingpotassium.jpg http://www.anticoagulation.com.au/portals/0/diet-01.png http://drwillard.com/blog/2015/01/all-you-need-to-know-about-vitamin-c/ https://s-media-cacheak0.pinimg.com/736x/67/d0/7b/67d07b12f8a1da9c1373bd5c03f4a126.jpg http://uvmdining.tumblr.com/post/112043637036/nutrition-insight-vitamin-d-andmushrooms http://www.rosannadavisonnutrition.com/best-plant-based-sources-calcium/ http://healthandwellnessmentor.com/protein-why-from-where-and-how-much/ https://thefusefitness.wordpress.com/tag/healthy-eating/ Nutrition notes Google Images