B5 - ChemistryIBWYA
advertisement

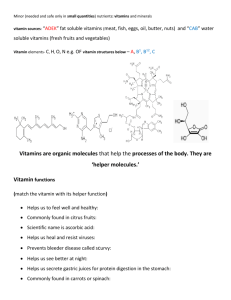
By Zhi Wei & John Substance which are required in small quantity for normal body function e.g. minerals & vitamins. Required ﹤0.005% of body weight Do NOT produce energy Very small amount of inorganic ions required for the function of the body Used for STRONG bones and teeth e.g. Ca, Mg & P; formation of hormones, enzymes; and maintaining of fluid levels. Organic compounds required for metabolism, to protect health and for proper growth in children. Vitamins generally are catalysis, which combines with proteins to create enzymes Various vitamins are not chemically related and most differ in their structures and physiological action Fat soluble vitamins (e.g. A, D, E & K) ◦ Contain Long hydrocarbon groups Water soluble vitamins (e.g. B & C) ◦ Contain highly polar OH groups Conformers: ◦ they are isomers which differ only in rotation around a single bond. Vitamin A ◦ Long carbon chain, one OH group and alternate double and single bonds ◦ Fat soluble ◦ light sensitive due to many conjugated double bonds Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) ◦ Five-membered ring containing an O atom; four OH groups Substance that are required in relatively large amounts (﹥0.005% of body weight) E.g. proteins, fats, carbohydrates and minerals (Na, Mg, K, ca, P, S and Cl) Macronutrients such as proteins, fats and carbohydrates produce energy Malnutrition: the insufficient, excessive or imbalanced consumption of nutrients. Income disparities, lack of economic opportunities and poor eating habits and so on Micronutrients affect Iron (Fe) aneamia (blood disorder) Iodine (I) goitre (enlarge of thyroid gland) Retinol (vitamin A) Causes dry eyes; night blindness Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) Scurvy (bleeding lesions on the legs) Calciferol (vitamin D) Softening of bones Macronutrients affect Proteins Adema (swelling), fatigue, muscle weakness, slow growth Calcium Ca osteoporosis Sodium Na cramps