Micro- and Macro- nutrients
advertisement

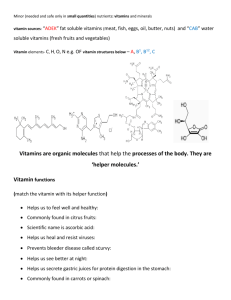
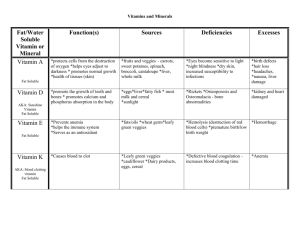
Micro- and Macro- nutrients Required health for good Micronutrients Required in very small daily amounts (mg) < 0.005% body weight Do not produce energy (like water) Co-factors with enzymes Vitamins and trace minerals (Fe, Cu, F, Zn, I, B, Co, Mo) Macronutrients Required in larger amounts (> 0.005% body weight) Proteins Fats Carbohydrates Minerals (Na, Mg, K, Ca, P, S, Cl) Vitamins Required for metabolism, good health and proper growth Help in formation of blood cells, hormones nervous tissue Fat soluble or water soluble Only Vitamin D can be synthesised by body Vitamin A (retinol) Fat soluble primary alcohol Can be stored in body’s fat, therfore not needed to be eaten every day Light sensitive (conjugated system) Required in production of rhodopsin (in rods of retina) Can change conformation of molecules Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) Water Soluble Note hydrogen attached to electronegative O. Can hydrogen bond to water Cannot be stored in body fat Regular intake is required Vitamin D Fat or water soluble ? Fat soluble Body can synthesise it Causes of nutrient deficiencies Income disparities Poor eating habits Limited food supply Famine Malnutrition not helped by poor sanitation, lack of health sevices, poor literacy rates Examples of Micro-nutrient deficiencies Anaemia Goitre Xerophthalmia Pellagra Beriberi Scurvy Rickets (take notes using page 342) Examplesof Macronutrient deficiencies Marasmus Kwashiorkor Edema Fatigue Decreased immunity Osteoporosis Cramps Solutions to vitamin deficiency Food rations Adding nutrients to food Genetic modification Nutritional supplements Selenium supplements Iron rich food Questions Page 360