Nutrition Unit PACKET and Presentation Guidelines
advertisement
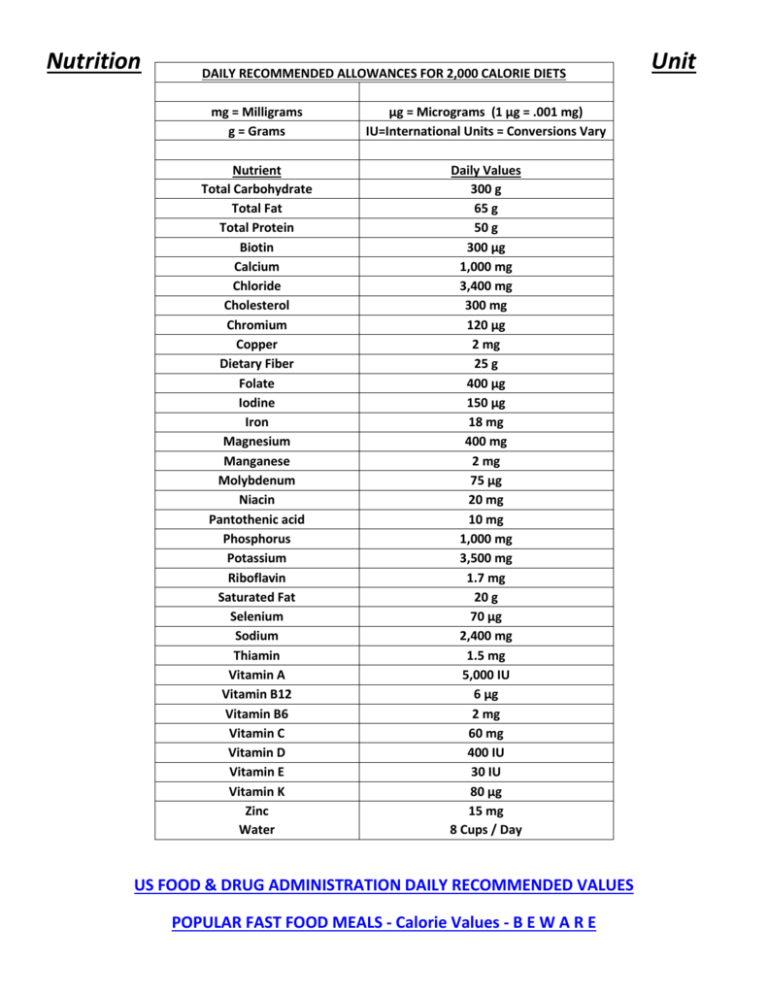
Nutrition DAILY RECOMMENDED ALLOWANCES FOR 2,000 CALORIE DIETS mg = Milligrams g = Grams µg = Micrograms (1 µg = .001 mg) IU=International Units = Conversions Vary Nutrient Total Carbohydrate Total Fat Total Protein Biotin Calcium Chloride Cholesterol Chromium Copper Dietary Fiber Folate Iodine Iron Magnesium Manganese Molybdenum Niacin Pantothenic acid Phosphorus Potassium Riboflavin Saturated Fat Selenium Sodium Thiamin Vitamin A Vitamin B12 Vitamin B6 Vitamin C Vitamin D Vitamin E Vitamin K Zinc Water Daily Values 300 g 65 g 50 g 300 µg 1,000 mg 3,400 mg 300 mg 120 µg 2 mg 25 g 400 µg 150 µg 18 mg 400 mg 2 mg 75 µg 20 mg 10 mg 1,000 mg 3,500 mg 1.7 mg 20 g 70 µg 2,400 mg 1.5 mg 5,000 IU 6 µg 2 mg 60 mg 400 IU 30 IU 80 µg 15 mg 8 Cups / Day US FOOD & DRUG ADMINISTRATION DAILY RECOMMENDED VALUES POPULAR FAST FOOD MEALS - Calorie Values - B E W A R E Unit Nutrition: The process in which the body takes in and uses food 6 Nutritents Carbohydrates Fat Protein Vitamins Minerals Water Water Daily Dietary % of Each Nutrient 45-65% 20%-35% 10%-35% see pg. 204-207 various minerals Men up to 13 Cups of fluid / day Women up to 9 Cups of fluid / day Calories Per Gram 4 cal/gram of carb 9 cal/gram of fat 4 cal/gram of protein 0 Calories 0 Calories 0 Calories 0 Calories I. Carbohydrates: The most efficient form of energy, the body transforms this nutrient into energy first 1. Types of Carbohydrates Simple (sugars) Complex (starches and Fiber) II. Fat: Provides us with energy, an essential nutrient, gives food flavor and texture 1. Types of fat Saturated: Animal fats tropical oils, Solid at room temp Unsaturated: Vegetable oils, olive oil, canola oil, Liquid at room temp Cholesterol: Fat manufactured by the liver, found in food of animal origin III. Protein: Also provides us with energy, but the major role is to maintain, build and repair cells. Our bodies can make 11 of the 20 amino acids. 1. Types of protein Complete: Animal proteins, contain all the essential proteins, the body needs 9 essential Incomplete: Plant proteins, lack some of the essential proteins IV. Vitamins: regulate the body’s processes 1. Types of vitamins Water soluble: dissolve in water, transported by the blood stream Fat Soluble: absorbed and transported by fats V. Minerals: inorganic substances the body can’t manufacture 1. Types of minerals Trace minerals: your body needs these in tiny amounts (iron, iodine, copper, zinc, and fluoride) still are very important Major minerals: your body needs 250 mg.+ per day (calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, sodium, potassium, chloride, and sulfur) IV. Water: Vital role in all your bodies processes: Water is your body's principal chemical component and makes up about 60 percent of your body weight. Every system in your body depends on water. For example, water flushes toxins out of vital organs, carries nutrients to your cells, and provides a moist environment for ear, nose and throat tissues. Nutrition Presentation Title Slide – What are you presenting? Slide 2 – What does your topic do in the body? Slide 3 – How does your topic interact with other topics? Slide 4 – Foods that your topic is in. Slide 5 – Summary (Putting it all together) Slide 6 – Your favorite food, what is good and bad about your food. Put food label on this slide and explain it. This does not relate to your topic. Hints: 1. Do not read off of power point (notes are OK to look at) 2. Be able to pronounce and understand any words that you present 3. On slide 6, point out what seems to be the up-side and/or down-side of your food choice - use the information from the food label for your food choice. (5 points) Grading Guidelines: A grade – Complete understanding of the topic B grade – Nice try and understood most of what was being presented C grade – At least you presented something F grade – Did not present anything











