Carbon Chemistry Powerpoint
advertisement

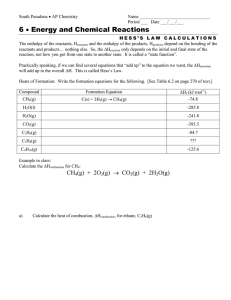
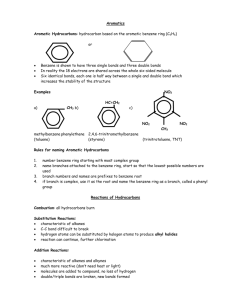
I. Let’s Talk About Carbon atoms have: •6 protons •6 neutrons •6 electrons (when neutral) CARBON!! + + + + + + Carbon atoms have 4 valence electrons, and they are all single C • Carbon atoms will always make 4 bonds. There are lots of ways to do this: 4 single bonds C OR 2 singles and 1 double 2 doubles C OR 1 single and 1 triple C C OR II. So how does Carbon work? A. There are many different forms: •Graphite A. There are many different forms: •Diamond A. There are many different forms: •Amorphous A. There are many different forms: •Buckminsterfullerene B. Carbon in Compounds •A hydrocarbon is a compound containing the elements carbon and hydrogen •Carbon forms the skeleton of each molecule •The hydrogens collect on the outside C2H6 CH4 H C H H H H H C H H H C H C C H H H C4H10 C3H8 H H C H H H H H H C C C C H H H H H H H C. Naming Hydrocarbons • If all the carbons are single bonded, the skeleton is holding as many hydrogens as it can, so it is saturated we call this type of hydrocarbon an alkane • The prefix is based on the number of carbon atoms • If it is saturated, the ending is “-ane” “pre” fixes One Meth- Five Pent- Nine Non- Two Eth- Six Hex- Ten Dec- Three Prop- Seven Hept- Four But- Eight Oct- Name the following: 1. CH4 2. C2H6 3. C3H8 4. C4H10 5. C6H14 6. C8H18 1.Methane 2.Ethane 3.Propane 4.Butane 5.Hexane 6.Octane What happens if we add a double or triple bond? We call them unsaturated • Alkenes - hydrocarbons containing a double bond • Alkynes - hydrocarbons containing a triple bond H H H C C H H H Ethane H H C H C H Ethene H Ethyne H H C C H H H C C C H H Propene E. Properties of hydrocarbons • Because they are nonpolar they don’t dissolve in water. • The forces that hold them together are weak so most are gases or volatile liquids at room temperature. • Many are flammable - coooool! F. Is there only one way to make C4H10? NO! H H H H CH3 H C H C H C H C H H CH3 CH CH3 •These are the two isomers of C4H10 G. Carbon chains • How many bonds does carbon like to make? • 4 • Carbon is good at making long chains also. This results in many properties: – Elastic - able to stretch and return to original shape – No definite melting point – Able to take any shape G. Carbon Chains • Examples of polymers: – Plastic and rubber • Biological molecules like proteins , fats and starches Which is which?