Presentation ( - 3.6mb)

Earthquake forecasting using earthquake catalogs
“Since my first attachment to seismology, I have had a horror of predictions and of predictors.
Journalists and the general public rush to any suggestion of earthquake prediction like hogs toward a full trough.”
- Charles Richter (1977)
Whoever wishes to foresee the future must consult the past;
Turn to you partner and discuss this statement
1) What does it mean?
2) Provide an example where it applies
3) Could this statement connect to earthquakes? How?
Earthquake Prediction vs.
Earthquake Forecasting
Earthquake Prediction = a short-term (hours to days) statement that an earthquake of a specified size will occur at a given location.
Earthquake Forecast = a long term (years to decades) statement of the probability of an earthquake in a region
(or the probability of one or more earthquakes in a region).
IRIS Earthquake Browser www.iris.edu
>For Educators
Looking for seismicity patterns
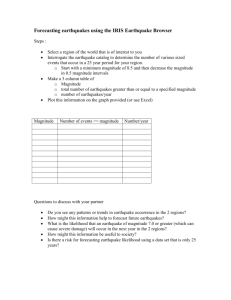
Steps :
• Select a region of the world that is of interest to you
• Interrogate the EQ catalogue to determine the number of various sized events that occur in a 25 year period for your region. (Start at min 9.0 and use M 0.5 intervals)
– Make a 3 column table of
• Magnitude
• total number of earthquakes greater than or equal to a specified magnitude
• number/year
• Plot this information on the graph provided (or use
Excel)
IRIS Earthquake Browser www.iris.edu
>For Educators
Looking for seismicity patterns
Steps :
• Select a region of the world that is of interest to you
• Interrogate the EQ catalogue to determine the number of various sized events that occur in a 25 year period for your region. ( Start at min 9.0 and use M 0.5 intervals)
– Make a 3 column table of
• Magnitude
• total number of earthquakes greater than or equal to a specified magnitude
• number/year
• Plot this information on the graph provided (or use Excel)
How might this information help to forecast future earthquakes?
Questions to discuss with your partner
• Do you see any patterns or trends in earthquake occurrence in the 2 regions?
• What is the likelihood that an earthquake of magnitude 7.0 or greater (which can cause severe damage) will occur in the next year in the 2 regions?
• How might this information be useful to society?
• Is there a risk for forecasting earthquake likelihood using a data set that only goes back to 1973?
Earthquakes, Magnitude >3.5, 1973-2007
Earthquakes,
Magnitude >3.5,
1973-2007
Questions
• What is the likelihood that an earthquake of magnitude 7.0 or greater will occur in the next year in the 2 regions?
• How might this information be useful to society?
• Is there a risk for forecasting earthquake likelihood using a data set that only goes back to 1973?
1000.00
What is the probability of an M6 event next year?
California
Gutenberg-Richter Plot
Eastern US Expon. (California) Expon. (Eastern US)
100.00
10.00
1.00
0.10
0.01
3.5
4 4.5
5 5.5
6
Magnitude
6.5
7 7.5
8 8.5
1000.00
What is the probability of an M7 event next year?
Gutenberg-Richter Plot
California Eastern US Expon. (California) Expon. (Eastern US)
100.00
10.00
1.00
0.10
0.01
3.5
4 4.5
5 5.5
6
Magnitude
6.5
7 7.5
8 8.5
Are the numbers of earthquakes in the smallest and largest ranges consistent with the trends in the other regions?
Can you think of any reasons why the trend is “flat” for small and also large magnitudes?
1973-2007
10 -3
10 -4
10 -5
N
10 -6
10 -7
10 -8
10 -9
Magnitude
N = earthquakes per km 2 per yr
Ground shaking from a magnitude
6 earthquake in the east is approximately equivalent to that of a magnitude 7 earthquake in the west.
http://pasadena.wr.usgs.gov/office/hough/east-vs-west.jpg
2002 National Seismic Hazard Map
Although we can’t predict earthquakes (in the sense of predicting a specific time, location and magnitude)…
Earthquake Hazard Analysis
Global Seismic Hazard Map
We can estimate the probability that a given amount of ground shaking will occur during a given period of time at some location.
Japanese Folklore:
Earthquakes caused by giant Namazu .
Following the 1755 Lisbon earthquake on All Saint’s Day, the Spanish
Inquisition burned people at the stake to atone for the city’s sins.
Earthquake
Prediction:
Precursory Events
Ex/ 1989 Loma
Prieta Earthquake
Also: Resistivity, water pressure and well levels, geyser activity, changes in seismicity
Earthquake Prediction: Animal Behavior??
The exception: Feb 4, 1974: Haicheng, China
* Almost no details are known of this.
Another Approach: Forecasting
Seismic “Gap” Hypothesis
OLD Map of “Seismic Gap” Predictions
Parkfield was in correct place, but very late.
Northridge, Landers, Joshua Tree and Big Bear
Earthquakes were not even on this map!!!
“New York City Bear Gap” Hypothesis
Parkfield, California, showed evidence of the recurrence of similar-sized (M 6.0) earthquakes
In 1985 a 6.0 Parkfield earthquake was predicted with
95% confidence to occur by 1993.
Mean = (1966-1857)/5 = 22 years
Expected date = 1988
Didn’t occur until
2004
(16 years late!)
Was it a success?
Right size, right location, wrong date.
Paleoseismology
Extend earthquake history with geologic record
Sieh et al., 1989
M >7 mean = 132 yr s
= 105 yr
Estimated probability in 30 yrs 7-51%
However, even earthquake recurrence along plate boundaries is highly variable; probabilities hard to assess
M>7: mean = 132 yr s =
105 yr
Sieh et al., 1989
Estimated probability of next earthquake in 30 yrs is 7-51%
Random!
Elastic Rebound (Seismic
Gap) Theory?
NY City Bear Gap
Hypothesis?
Random seismicity simulation