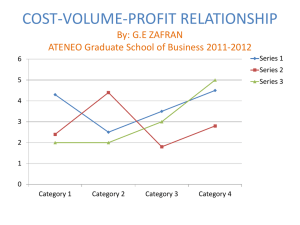
Cost, Volume, and Profit Questions
advertisement

COPYRIGHT NOTICE All text appearing in this document are protected by copyright. Redistribution or commercial use is prohibited without express written permission. Cost, Volume, and Profit Questions Mixed costs are classified in both the variable and fixed costs. Since mixed costs have elements that will change the outcome of total costs, a good method should be used to determine accuracy for future costs. A method management might use is the high and low method. It basically finds the difference between the total costs of high and low levels to find variable cost per unit. The CVP, or cost-volume-profit analysis is based on more than just unit costs. It examines the aspects and components on profits. The CVP analysis includes figuring out volume activity, unit selling prices, variable cost per unit, total fixed costs, and sales mix. The CVP analysis will take these components and determine the break even point as well as the profitable point. If the net income is negative, management will do things to make sure costs can be brought down and its duty is to bring the net income to its highest. In order to plot the break even point, management must determine the total costs and total sales. The point where the measure is the same is when it is unprofitable or known as break even point. By dividing the number of fixed costs and contribution margin ratio expressed as: fixed costs/ contribution margin ratio would equal break even point in dollars. The contribution margin ratio is determined by the contribution margin per unit divided by unit selling price. To determine the contribution margin per unit, subtract the unit variable cost from the unit selling price. A person can use this formula to graph the loss area, break even point, and the profit area.