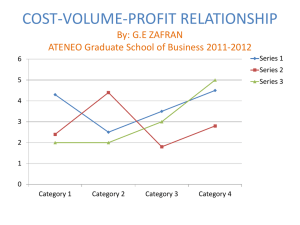
Cost
advertisement

Managerial Accounting 2011 First semester Takayuki Asada 1 Chapter4 Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis After reading this chapter, you will be able to: Identify common cost behavior patterns. Estimate the relation beween cost and activity using account analysis and the high-low method. Perform cost-volume-profit analysis for multiple products. Discuss the effect of operating leverage. Use the contribution margin per unit of the constraint to analyze situations involving a resourse constraint. 2 1. Introduction Mary Stuart is the vice president of operations for CodeConnet,a company that manufacturers and sells bar code readers. As senior mamanger,she must answer a variety of questions dealing with planning,control and decision making. Planning:Code Connect sold 20,000 bar code readers at $200 per unit. The cost of manufacturing these items was $2,940,000 ,and sellin g and administrative costs were $800,000. Total profit was $260,000. In the coming year,the company expects to sell 25,000 units. What level of profit should be in the budget for the coming year? Control:In April,production costs were $250,000. In May ,costs increased to $265,000,but production also increased from 1,750 units in April to 2,000 units in May. Did the manager responsible for production costs do a good job of controlling costs in May? Decision Making: The current Price for a bar code reader is $200 per unit. If the price is increased to $225 per unit, sales will drop from 20,000 to 17,000. Should the price be increased ? 3 2. Common Cost behavior patterns To perform cost-volume-profit analysis,you need to know how costs behave when business activity changes. This section describes some common patterns of cost behavior. 1).Variable costs:variable costs are costs that change in proportion to changes involume or activity. Thus,if activity increases by 10 percent,variable costs are assumed to increase by 10 percent. 2).Fixed costs:Fixed costs are costs that do not change in response to changes in activity levels. In the short run,some fixed costs can be changed while others cannot, discretionary fixed costs are those fixed costs that management can easily change in the short run. Committed fixed costs are those fixed costs that cannot be easily changed in a relatively brief period of time. 3). Mixed costs:Mixed costs are costs that contain both a variable cost element and a fixed cost element. These costs are sometimes referred to as semivarible costs. 4 4)Step costs: Step costs are those costs that are fixed for a range of volume but increase to a higher level when the upper bound of the range is exeeded. 3. Cost estimation methods In order to predict how much cost will be incurred at various activity lelvels, You must know how much of the total cost is fixed and how much is variable. In this section,we cover three techniquies for estimating the amount of fixed and variable cost : account analysis ,hight-low method, and regression analysis. 1)Account analysis:The method requires that the manager use professional judgement to classify costs as either fixed or variable. The account analysis methid is subjective in that different managers viewing the same set of facts may reach different conclusions regarding which costs are fixed and which costs are variable. 5 2) Scattergraphs: Suppose the monthly production and cost information provided in illustration 4-7 is available for CodeCOnnect. We can gain insight into the relation between production cost and activity by plotting these costs and activity levels. The plot of the data is referred to as a Scattergraph. 3)High-Low Method:With the same type of data as that described previouly,we can estimate the fixed and variable components of cost at various activity levels using the high-low method. 6 4)Regression Analysis Different costs for different purposes. This suggest that there is no universal way to compute the cost of something. Management accountants define and compute costs that reflected identified decision making needs. 5) Relevance range: when working with estimates of fixed and varible costs, remember that they are only valid for a limited range of activity. Regression anasysis is a statistical technique that uses all the available data points to estimate the intercept and slope of a cost equation. 7 4.Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis: How the use of product cost information defines its focus and form 1)Financial accountants and management accountants define and think about cost very differently , particulary product costs. 2)Using product cost information outside the organization Since no one knows how the investors,etc. use the costs numbers in financial statements, generally accepted accoutning principles that specify the focus,content and form of financial statements focus on methods for computing costs rather than how they might be best calculated to support a given decision. 3)The profit equation The profit equation states that profit is equal to revenue (selling price times quantity),minu variable cost ,minus total foxed 8 cost. Using Cost information to predict costs and profits Cost-Volume-Proft Analysis is a procedure for combining information about variable and fixed costs with revenue information for different levels of volume. Profit=revenue- costs (4.1) Profit = Revenue-variable costs – fixed costs (4.2) Profit=(units sold × revenue per unit) – (units sold × variable cost per unit) – Fixed costs (4.3) Profit = (unit sold × (revenue per unit – variable cost per unit) ) – fixed costs (4.4) Profit = (units sold × Contribution margin per unit ) –fixed costs (4.5) Units required to earn a target profit = (target profit + fixed (4.6) cost) / contribution margin per unit Breakeven unit sales = Fixed costs / contribution margin per unit (4.7) units required × revenue per unit = (target profit + fixed cost) × revenue per unit / contribution per unit margin per unit (4.8) Revenue required = (target profit + fixed cost ) / contribution margin ratio (4.10) Breakeven sales revenue = Fixed cost / contribution margin ratio (4.11) 10 Expenditures,Costs and Expenses Expenses are the costs of assets that the financial accountants deems have been used up when goods or services are sold. Product Costs for manufacturing firms,financial accoutants include only manufacturing costs in the cost they report for product inventory,and threfore,as the expense they report for the goods sold. in summary,for a manufacturing firms, product cost reported on the balance sheet include only manufacturing costs ad almost always reflected historical costs. Using Product Cost Information inside the organization two broad categories which mean Planning and evaluation 1)Selling price based on cost as a reference point 2)budgeting use 3)planning and control use 11 .Understanding Cost Behavior to Predict Costs understanding cost behavior allows the management accountants to develop estimates of product costs and to predict costs for various levels of production activity. you can understand the different behavior of cost when you know the notion of flexible resources and capacity related resouces. The cost of flexible resourses are called variable costs. Capacity-related resources are acquired and paid for in advance of when the work is done. The costs associated with capacity-related resources are called fixed costs. 12 The CVP Chart: Executives ,analysts,and regulators track average yield and load factor for the industry and each airline very varefully since small changes in the load factor have large effects on profits(since fixed costs make up most of the total costs ,the total cost curve has a small slope) and since most airlines operate near their breakeven load factor as shown in the practice box(p.40). 13 Extending CVP analysis for multiproduct organizations Lynn’s Landscaping Services,Lynn would construct an average product by weighting each of her company’s three real products-lawn mowing,layout design, and other maintenance-by their respective proportions in the estimated product mix. Exhibit 2-6 Lawn Mowing Layout Design unit total unit Total Units sold 4600 350 Revenues 50,000 230,000 500 175,000 Variable costs 27.17 125,000 160 56,000 80,153 Fixed Costs 105,343 Profit -343 38,847 Other maintenance Unit Total 1250 200 250,000 116 145,000 114,504 -9,504 14 Exhibit 2-7 Lynn’s Landscapeing Services:Composite Product Calculation Lawn Moving unit %Total Unit Sold 4,600 74.193548% unit Revenue 50.0 Variable costs 27.17 Contribution Margin Layout Design Other Maintenance Total unit %Total Unit %total 350 5.645161% 1,250 20.161290% 6200 weight unit weight unit weight total all 37.10 500.00 28.23 200.00 40.32 105.65 20.16 160.00 9.03 116.00 23.39 52.58 53.06 Noting that the total fixed costs at Lynn’s Landscaping is 300,000(105,343+80,153+ 114,504) ,use the breakeven formula (equation 2.7) to compute the breakeven level of sales for this composite product: Breakeven = Fixed cost / contribution margin per unit = 300,000/53.06 (2.15) unit sales 15 To summarize ,CVP analysis provided decisions makers with a handy ,flexible and convenient way to model the relationship between volume and profits. 16 Using Cost Information to develop Product Costs We are faced with the problems of how to incorporate fixed costs into a product cost. 1)A widely used approach is to divide fixed costs by the number of units actually produced. This has the nice effect of including all the fixed costs in the product costs,but it has the unfortunate effect of increasing the computed cost of a product as demand goes down. 2)An alternative approach to including fixed costs in product costs is to divide the fixed cost by the practical level of capacity provided to get a cost per unit of capacity. 17 5.Multiproduct Analysis The previous examples illustrates CVP analysis for a single product. But CVP analysis can be extended to cover multiple products. 1)Contribution margin approach: 2)Contribution margin ratio approach 18 6.Assumptions in CVP Analysis 19 7. Code Connect Example reviseted Mary’s questions 20 8.Operationg Leverage 21 9.Constraints 22 Summary 23