Parts of the cell
advertisement

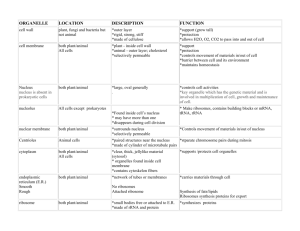
Parts of the cell Chapter 7.3 Prokaryotes (bacteria) • Nucleoid- control center that does NOT have a membrane around it and holds the DNA • Cytoplasm- the liquid “goo” that everything in the cell sits in • Ribosomes- protein factories that build the proteins for the cell • Plasmid- packets of DNA that the bacteria can swap with other bacteria to make it more resistant to medicine • Cell membrane- regulates the transport of substances in and out of the cell • Cell wall- rigid outer structure that protects the cell and gives it structure • Capsule-slippery layer of the cell that keeps it from drying out and helps it slip away when phagocytes try to engulf it • Pili- help bacteria attach to surfaces • Flagella- whip like tail for movement Nucleus (control center) • The nucleus is located in the center of the cell – ___________________________________ – Is the control center(brain) of the cell • The nucleus is broken down into parts – Nucleolus- _________________________________________________ – _______________________membrane that covers the nucleus – ______________openings in the nuclear membrane that allow things in Ribosomes (protein factories) & ER • ____________________ the little dots found in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum that make proteins for the cell • Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): work with ribosomes to make proteins – __________________________________________________________ – The folds increase the surface area for cellular functions to take place • ____________________ER with ribosomes attached to the outside surface. – Makes it bumpy looking or rough – __________________________________________________________ • Smooth ER- ER with no ribosomes attached, responsible for making lipids Both package and deliver new proteins and lipids via vesicles to the Golgi apparatus. Golgi Apparatus (FED-EX) • Golgi Apparatus- __________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ – Looks like a stack of pancakes – Receives newly made proteins and lipids from the ER which it then modifies, repackages (in vesicles) and distributes to the rest of the cell • ____________ (transporters)- membrane bound transporters that take proteins and other packages around the cell and out of the cell Vacuoles (containers) • Vacuoles(containers)- ________________________________________ – Common in plant cells (central vacuole), ____________________________ – Also found in single celled eukaryotes as a “contractile vacuole” which pumps excess water out of the cell. • Lysosomes (___________)- small membrane bound sacs that are filled with digestive enzymes and they wander around the cell dissolving nutrients in the cell or “lysing” ______________________________________________ • Centrioles- ___________________________________________________ Vacuoles can take up to 30% of a plant cell’s volume Pathway of particles • Ribosomes found on the rough ER make LOTS of proteins • ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ • The vesicle dumps the protein off at the Golgi Apparatus and dissolves into the Golgi’s membrane • The proteins get repackaged by the __________________________ __________________________________________and some products get stored in the vacuole Enough about transport, how do cells get their energy???? Chloroplasts & Mitochondria (POWERHOUSES) • Chloroplasts- ________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ – The stacks of green discs are the actual structures that produce the all of the energy through photosynthesis • ________________chili bean looking structures that produce energy for plant and animal cells – Makes ATP (packets of energy) for the cell to use – Site of ____________________ Skeleton & Movement • Cytoskeleton- ____________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ – Like the steel beams of a building that give it strength • ________________rigid straight tubes that act as structural support • ______________thin protein thread/webs that help give cells shape • Flagella- _________________________________________________ • Cilia- ___________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ Outer Barrier • Plasma membrane- ___________________________________ ____________________________________________________ • ________rigid outer most layer of plant cells made of cellulose, provides structure for the plant Working together • All of the organelles in the cell have very different jobs but they all work together to make the cell function properly. Animal Cells vs Plant Cells