The “brains” of the cell, that directs cell activities and contains
advertisement

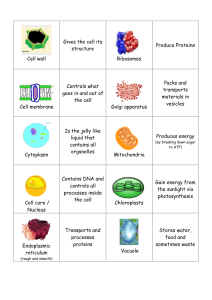
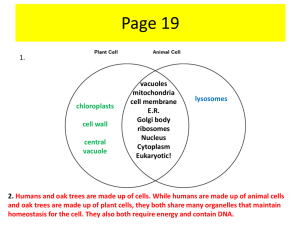
Convert sugar into energy 1 mitochondria 2 Make proteins for just the cell they are located within 3 Free ribosomes 4 Make cell parts more efficient by increasing the available space for work to take place within a cell 5 Folded membranes 6 Package and distribute proteins 7 golgi 8 Contains digestive enzymes to help break down cell wastes 9 lysosomes 10 Act like little UPS trucks as they deliver the packages (proteins) 11 golgi 12 Uses sunlight to produce sugars (food) for plant cells 13 chloroplasts 14 Energetic cells need a lot of these to make ATP 15 mitochondria 16 Act like little garbage trucks to move around, pick up cell waste, and get rid of it 17 lysosomes 18 Stores wastes, nutrients, and water 19 vacuole 20 Encloses the nucleus like an envelope 21 Nuclear membrane 22 Site of photosynthesis 23 chloroplast 24 Rigid outermost layer in plant cells 25 Cell wall 26 Larger storage organelle in plant cells than in animal cells 27 vacuole 28 "intracellular highway" because it is used for transporting proteins from the ribosomes 29 Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) 30 The “brains” of the cell, that directs cell activities and contains genetic material called chromosomes made of DNA 31 nucleus 32 Allow ribosomes and genetic material to move through the nuclear membrane 33 Nuclear pores 34 Make proteins to be transported outside of the cell they are produced within 35 Ribosomes on the endoplasmic reticulum 36 The framework that anchors organelles within the cytoplasm 37 cytoskeleton 38 Works with the cell wall to maintain turgor pressure within plant cells 39 vacuole 40 Cells that do not have nuclei (plural version of nucleus) 41 prokaryotes 42 Cells that have nuclei, organelles such as chloroplasts, and cell walls made of cellulose 43 eukaryotes 44 Chloroplasts and mitochondria both convert this 45 energy 46 Regulates what enters and exits the cell 47 cell membrane 48 Bacteria cells for example 49 prokaryotic cells 50