Cell Parts - Wood-Ridge School District / Homepage
advertisement

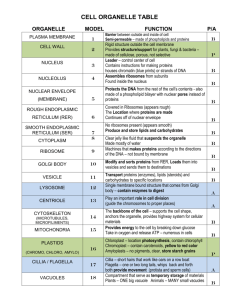
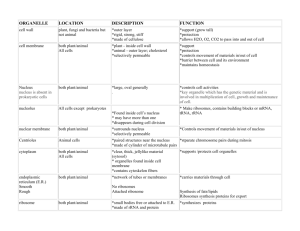
Eukaryotes Cell (Plasma) Membrane Selectively permeable membrane- regulates what H2O is polar enters/leaves the cell Composed of 2 layers of specialized lipids (called phospholipids), proteins, and carbohydrates Separates internal and external environments Phospholipid - Phospholipid bilayer Cell Wall Rigid structure OUTSIDE of the cell membrane in plant cells. Provides shape and protection Plant cell walls – mostly cellulose Which organic compound is cellulose? Prokaryotic cell walls- peptidoglycan Contain openings (plasmodesmata) that materials (H2O and small molecules) can move through to neighboring cells **NOT found in animal cells** Vacuoles Central Vacuole- A Large, membrane-bound compartment that stores ions, nutrients, and wastes. Contributes to plant growth when full Contractile Vacuole-some unicellular eukaryotes (freshwater algae) use them to pump out excess water. Allows them to regulate concentration of salts & other molecules. Food Vacuole- formed when cell membrane surrounds food particles outside the cell and draws them into the cell. Lysosomes fuse with food vacuoles and digest the food particles. Some central vacuoles found in leaf cells contain poisons that offer protection against plant-eating animals. Others contain the pigments giving flowers color which attracts pollinating insects. Nucleus Control center, boss, or “brain” of the cell Contains the genetic material (DNA) in eukaryotic cells Surrounded by a thin double membrane called the nuclear envelope. Nuclear Pores- small openings in the nuclear envelope that allow substances made in the nucleus to move out into the cytoplasm. Nucleolus Site of ribosome part, or subunit, production. Q: How could ribosome parts enter the cytoplasm from within the nucleus? Composed of DNA, RNA, and proteins. Disappears at start of cell division and reappears at the end. Ribosomes Synthesize (make) proteins – “ protein assembly lines” Small organelle composed of RNA and proteins Locations within cells: 1. 2. 3. Endoplasmic reticulum-RER (bound) Nuclear membrane (bound) Cytoplasm (free) Free ribosomes- make proteins that remain inside the cell, such as proteins that build new organelles or enzymes used to speed up reactions. Bound ribosomes- make proteins to be released from the cell Note: Ribosomes can switch between free and bound states depending on the type of protein that the cell needs. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Network of membranes that form a transportation route for materials Synthesizes many molecules for transport Connected to the outer membrane of the nuclear envelope Rough ER- studded with ribosomes Smooth ER- NO ribosomes. Contains various enzymes enabling the SER to carry out different functions Ex: Lipid synthesis. To the Golgi Receive, Package, Deliver “receiving dock” for vesicles animation Enzymes refine and modify vesicles Vesicles travel to specific parts of cell Golgi Apparatus Receives products (Ex: proteins & lipids) from ER contained in vesicles Arranged in pita bread-like stacks Modifies, stores, and routes them to their next destination. Golgi enzymes chemically refine and modify ER products. Path of Proteins in Eukaryotes Ribosomes bound to the rough ER make proteins directly into the ER. The rough ER membrane pinches off forming a vesicle around the protein. Vesicles carry the proteins through the cytoplasm to the golgi apparatus where they fuse with the golgi. Enzymes within the golgi modify the proteins as they move through. On the other side, the finished proteins (enclosed in NEW vesicles) that bud from the golgi apparatus. Vesicle membrane fuses with cell membrane- releasing proteins outside the cell. Path of Proteins in Eukaryotes Endocytosis Exocytosis Mitochondria Site of cell respiration- Food energy used to make ATP “Energy Factory” or “Powerhouse” of the cell Found in almost every eukaryotic cell Two membranes: Inner membrane – folding increases surface area for ATP-producing enzymes to act on. Outer membrane Cell type determines number of mitochondria Lysosomes Membrane-bound sacs containing digestive enzymes that break down large molecules. Ex: nucleic acids, proteins, and polysaccharides Fuse with food vacuoles to digest contents and nourish cell. “Cellular Safety Officers”- WBC lysosomes release enzymes into vacuoles containing bacteria. Why? “Recycling Centers”- Engulfs and digests old, unused, or damaged organelles. Molecules become available for constructing new organelles. Chloroplast Site of photosynthesis: Light energy used to make sugar from CO2 and H2O. Light energy Chemical (food) energy NOT FOUND IN ANIMAL CELLS Found in plants and algae Surrounded by a pair of membranes. Disks (within the inner membrane) are the chloroplast’s solar “power packs”- allow them to trap solar energy Green color results from the pigment chlorophyll Cytoskeleton Cytoskeleton- web of protein fibers that provide support to the cell. Fibers making up the cytoskeleton: 1. Microtubules: thick, hollow tube of protein subunits (parts) that provide rigidity, shape, and organization to cells. Made up of the protein tubulin. • Provides “tracks” for organelles to move • Ex: Lysosome may reach a food vacuole using microtubules. 2. Intermediate Filaments- moderately thick, anchor organelles & enzymes to certain parts of cell. 3. Microfilament: solid rod of protein, thinner than microtubules, that enables a cell to move or change shape (Ex: amoeba) 1. Made up of the protein actin. Cell-Factory Analogy Cell-Factory Analogy Cell-City Analogy The Cell Song: http://youtu.be/rABKB5aS2Zg A Tour Of An Animal Cell: http://youtu.be/4DWaAIVlW3k Inner Life Of A Cell: http://youtu.be/B_zD3NxSsD8