Cellular Organelles
advertisement

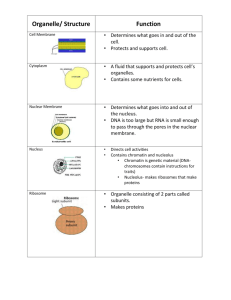
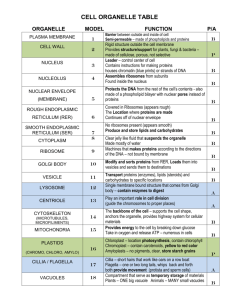
Cellular Organelles 6.3 & 6.4 Organelles covered today Nucleus & nuclear envelope Ribosomes Endomembrane system Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Golgi apparatus Lysosomes Vacuoles Nucleus - Structure Contains the DNA packaged into genes on chromosomes Nuclear envelope is a double membrane that separates nucleus from cytoplasm Pore complex lines each nuclear pore and regulates entry & exit (RNA leaves through the pores) Nuclear lamina lines inner surface & help maintain shape Nuclear matrix is a framework of fibers extending throughout the interior of the nucleus Organization of DNA DNA is organized into discrete units called chromosomes Each chromosome is made up of chromatin (complex of proteins and DNA) Chromatin is the uncoiled form of DNA Chromosomes is the coiled up form of DNA that takes shape when the cell is about to divide Chromosome Number Every human cell has 46 chromosomes that occur in pairs called homologous pairs So we have 23 homologous pairs of chromosomes The exception is the sex cells or gametes (sperm & egg) which have 23 chromosomes. This preserves chromosome number from one generation to the next Nucleolus Structure in the non-dividing nucleus – appears as a mass of densely stained granules and fibers Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is synthesized from instructions contained in the DNA Proteins imported from the cytoplasm are assembled with rRNA into large and small ribosomal subunits Small & large subunits exit nucleolus where they can assemble proteins Ribosomes Made of ribosomal RNA and proteins Main function: carry out protein synthesis Cells that make a large number of proteins have a high percentage of ribosomes (example: pancreas) Two types of ribosomes – both contain large & small subunits Free ribosomes – suspended in the cytoplasm and make proteins that function within the cytoplasm Bound ribosomes – attached to the outside of the ER and make proteins that are inserted into membranes or exported from the cell. Endomembrane system Functions in the cell: Synthesis of proteins Transport of proteins into membranes or out of the cell Metabolism and movement of lipids Detoxification of poisons System is connected through direct contact or by transfer of vesicles Organelles of the Endomembrane system: nuclear envelope, ER, Golgi, lysosomes, vacuoles, plasma membrane Endoplasmic Reticulum Extensive network of membranes that is continuous with the nuclear envelope (surrounds it) Two sections of the ER Smooth ER – contains no ribosomes Rough ER – surface is covered with ribosomes Smooth ER Functions of the Smooth ER: Synthesis of lipids (oils, phospholipids, steroids) Metabolism of carbohydrates Detoxification of drugs and poisons by adding hydroxyl groups to make them more soluble and easier to flush from the body How does this relate to addiction? More drugs & alcohol = more smooth ER and enzymes to increase the rate of detoxification. This increases tolerance to the drugs which means you need more of it to achieve desired effect. Rough ER Functions of Rough ER Transport of proteins out of the cell Ribosomes are attached that undergo protein synthesis Make proteins that will be secreted from the cell These proteins leave ER in a vesicle (little vehicle) Membrane factory for the cell It grows in place by adding membrane proteins and phospholipids to its own membrane Golgi Manufacturing, warehousing, sorting, and shipping center for the cell Products of the ER are modified and stored and then sent to their final destination Consists of flattened membranous sacs Vesicles are concentrated around the golgi bringing things to it and away from it Sides of the Golgi The golgi has two sides to it: Cis face – receiving department Side facing the ER Trans face – shipping department Side facing the plasma membrane Proteins come from the ER in transport vesicles and fuse to the Cis face and are modified and leave in vesicles from the trans face (alphabetical order C – T) Lysosomes Sac of hydrolytic enzymes that an animal cell uses to digest macromolecules Sacs are highly acidic and enzymes are designed to work best there If a sac breaks open no damage is done because cytoplasmic pH is neutral Made by the rough ER Intracellular digestion of nutrients & damaged organelles Disorders: Tay-Sachs – a lipid digesting lysosome is missing and the brain becomes impaired by lipid buildup. Vacuoles Compartments for storage Types: Food vacuoles Contractile vacuoles (water pumps) Central vacuoles (water storage in plants) Central Vacuole Tonoplast surrounds the central vacuole Stores organic compounds Stores potassium & chloride (inorganic compounds) Disposal sites for harmful compounds Contain pigments that color the cells to help attract pollinators Contain poisonous compounds to help protect against herbivores Major role in the growth of plants Review of the Endomembrane System