Classification
advertisement

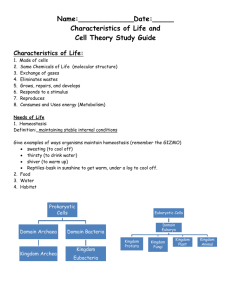
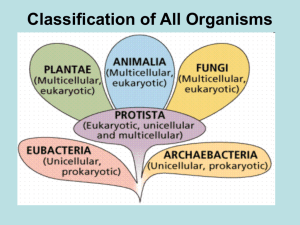
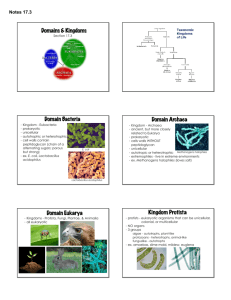
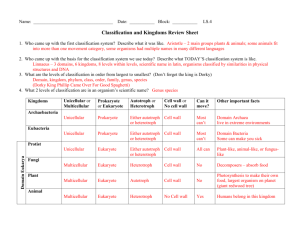
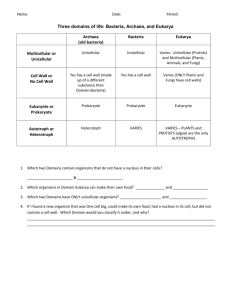
Classification EVOLUTION UNIT Devil Cat Ghost Cat Mountain Lion Screaming Cat Puma Florida Panther Cougar There are at least 50 common names for the animal shown on the previous 7 slides. Common names vary according to region. •Soooo……why use a scientific name? Carolus Linnaeus Swedish botanist that developed a two-word naming system (binomial nomenclature) and a classification system which includes seven Hierarchical taxa. Linnaeus Seven Hierarchical Taxa: The major classification levels, from most general to most specific. (several of these have subdivisions) A group at any level is a taxon. Example: Grizzly Bear Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata Class Mammalia Order Carnivora Family Ursidae Genus Ursus Species Ursus arctos Cladogram Diagrams that shows the evolutionary relationships between living organism. Domains and Kingdoms Organisms are placed into domains and kingdoms based on: their cell type their ability to make food number of cells that make up the organism. The Three Domains Domain – – Archaea Includes newly discovered cell types Contains 1 kingdom – the Archaebacteria Domain Bacteria – Includes other members of old kingdom Monera – Has 1 kingdom – the Eubacteria Domain Eukarya - Includes all kingdoms composed of organisms made up of eukaryotic cells – Protista – Fungi – Animalia – Plantae Domain: Bacteria Kingdom: Eubacteria Cell Type: Prokaryote (lacks a nucleus) Cell Structure: Cell walls with Peptidoglycan # of Cells: Unicellular (organisms consists of a single cell) Mode of Nutrition: Autotroph or Heterotroph Example: E. Coli Domain: Archaea Kingdom: Archaebacteria Cell Type: Prokaryote (lacks a nucleus) Cell Structure: Cell walls without Peptidoglycan # of Cells: Unicellular (organisms consists of a single cell) Mode of Nutrition: Autotroph or Heterotroph Example: Halophiles Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: Protista Cell Type: Eukaryote (Cells with a nucleus) Cell Structure: Some cell walls with cellulose; some chloroplasts # of Cells: Most unicellular; Some colonial; some multicellular. Mode of Nutrition: Autotroph or Heterotroph Example: Amoeba, Slime Molds Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: Fungi Cell Type: Eukaryote (Cells with a nucleus) Cell Structure: Cell walls of Chitin # of Cells: Most multicellular; some unicellular Mode of Nutrition: Heterotroph Example: Mushrooms, yeast Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: Plantae Cell Type: Eukaryote (Cells with a nucleus) Cell Structure: Cell walls of cellulose; chloroplasts # of Cells: Most multicellular; some green algae unicellular Mode of Nutrition: Autotroph Example: mosses, ferns Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: Animalia Cell Type: Eukaryote (Cells with a nucleus) Cell Structure: No cell walls or chloroplasts # of Cells: Multicellular Mode of Nutrition: Heterotroph Example: Sponges, worms, insects, fish, mammals