classification part 1 for blog
advertisement

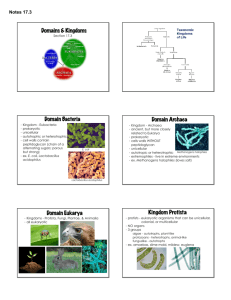
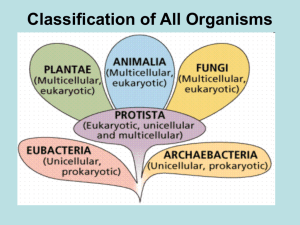
CLASSIFICATION NOTES Classification- A grouping of objects or information based on similarities Taxonomy- the branch of biology concerned with the grouping & naming of organisms Aristotle:384-322 BC First method of classification 2 major groups Plants - size & structure Animals - where they lived (land or water) Linnaeus: 1707 - 1778 Still used today Based on physical characteristics, close relationships 7 Levels of classification 1. Kingdom 2. Phylum 3. Class 4. Order 5. Family 6. Genus 7. Species King Phillip Came Over From Great Scotland Taxon: a group at any level of organization. Figure 18-5 Classification of Ursus arctos Section 18-1 Polar bear Black bear Giant panda Red fox Coral Sea star Abert squirrel snake KINGDOM Animalia PHYLUM Chordata CLASS Mammalia ORDER Carnivora FAMILY Ursidae GENUS Ursus SPECIES Ursus arctos Go to Section: Binomial nomenclature: System that gives each organism 2 names Genus: 1st word, always capitalized. Group of closely related species species: 2nd word, lowercase. descriptive (latinized) Ex-Eurycea bislineata-2 line salamander common name varies from place to place • http://www.search.com/reference/Wile_E._ Coyote_and_Road_Runner Domain Archaea Kingdom Archaebacteria Prokaryotes - No nucleus or membranebound organelles Cell walls without peptidoglycan Unicellular Autotroph or heterotroph Examples: Methanogens, Halophiles Domain Bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Prokaryotes Cell walls with peptidoglycan No nucleus or membrane bound Organelles Unicellular Autotroph or Heterotroph E. Coli and Streptococcus Domain Eukarya Kingdom Protista Eukaryotic Cell walls in SOME (plantlike) with cellulose with chloroplasts Most are Unicellular some Multicellular Autotroph or heterotroph Paramecium, Kelp, Euglena Domain Eukarya Kingdom Fungi Eukaryote Cell wall with chitin, nucleus and membrane-bound organelles-no chloroplasts Most are multicellular Heterotroph Eats by absorbing nutrients Mushrooms, yeasts Domain Eukarya Kingdom Plantae Eukaryotes Cell walls with cellulose, have chloroplasts Multicellular Autotroph Mosses, ferns, trees, flowering plants Domain Eukarya Kingdom Animalia Eukaryote No cell wall or chloroplasts Have specialized systems Multicellular Heterotroph sponges, worms, insects, fish 1. This kingdom contains all autotrophic organisms. 2. The term autotrophic refers to… 3. The opposite of autotrophic is… 4. These organisms contain the material chitin… 5. These kingdoms contain prokaryotic cells… 6. Which is the most general of Linnaeus’ seven taxa? 7. If 2 organisms are in the same kingdom, must they belong to the same phylum? 8. If several organisms contain the same class characteristics, must they belong to the same phylum? 9. Linnaeus’ 2 name system is called… 10.The most specific part of a scientific name is the… 11. If 2 organisms belong to the same order, must they belong to the same family? 12.In the scientific name the first letter of the ___ must be capitalized. 13. The scientific name must be ____ or italicized.