A Look at Diversity
advertisement

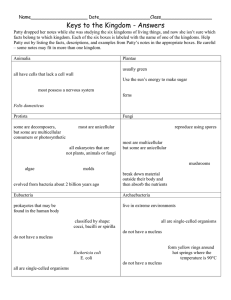
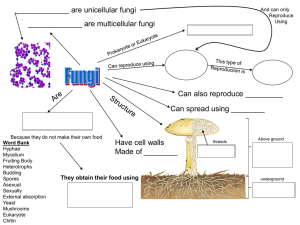
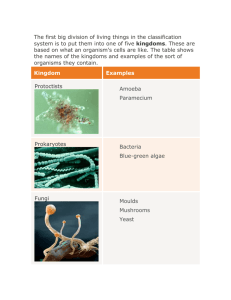
A Look at Diversity The Kingdoms of Life The Kingdoms • • • • • • Animalia Plantae Fungi Protista or Protoctista Archaea Eubacteria Kingdom Animalia • Multicellular – “made up of many cells” • Cells are eukaryotic (“true nucleus”) • Obtain food/energy by eating and digesting (“heterotrophic”) • MOST reproduce sexually • Can live in many different environments – Freshwater, soil, land, jungles, houses! • HUGE range of sizes – Microscopic worms to whales Kingdom Plantae • Multicellular • Cells are eukaryotic (“true nucleus”) • Obtain energy by converting sun energy into their own “food” a.k.a. photosynthesis (“autotrophic”) • Reproduce sexually! Really! • Can live in many different environments – Freshwater, soil, land, jungles, houses! • Come in diverse forms in a HUGE range of sizes – Mosses all the way to giant sequoias Kingdom Fungi • Also multicellular but some fungi (like yeast) are organisms made of a single cell • Obtain energy/food “opposite” from the way animals do…(still “heterotrophic”) • Can reproduce sexually or asexually, depending on what species • Hugely diverse! • Examples include penicillium, yeast, mushrooms, athlete’s foot, ringworm! Kingdom Protista • Live in water, moist habitats, soil, on trees, inside other organisms • Diverse ways that protists: – Reproduce – Obtain food/energy – Are shaped (and size varies, too) – Live their lives! • Diseases include malaria, giardia Kingdom Archaea (or Archaebacteria) • • • • Single celled. That means 1 cell = 1 organism Prokaryotic (“before” “nucleus” – so has none!) Come in many different shapes Lives in extreme environments – Low oxygen, high temperature, high salt, high acidity • Some obtain food/energy from the environment (“heterotroph”) and some can convert sun energy (“autotroph”) • Typically don’t move (no structures on body to allow movement) Kingdom Bacteria • • • • Single celled. That means 1 cell = 1 organism Prokaryotic (“before” “nucleus” – so has none!) Come in many different shapes Can live in any environment – soil, human bodies, water, dog poop! • Some obtain food/energy from the environment (“heterotroph”) and some can convert sun energy (“autotroph”) • Typically don’t move (no structures on body to allow movement) Kingdom Bacteria • Used for environmental clean-up efforts • Reproduce by dividing in two (to produce two “daughter” bacteria/cells) or budding • Some exchange small amounts of DNA • Prokaryotes (pro = “before”, karyon = “kernel”/“nucleus” Homework to complete after lecture • Bacteriophage • Pretty good lecture – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ycx_ClAcyc Debrief Questions 1. Which of the characteristics seems to be the most useful to biologists in grouping organisms into kingdoms? 2. How does this table address the following statement? All living things show unity and diversity. 3. Analyze your table for three trends that go from left to right and write them descriptively.