Kingdoms and Domains
advertisement

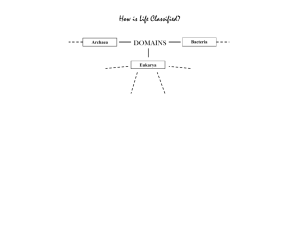
Kingdoms and Domains Differences and Similarities Why do we put that there? REMEMBER Cell without a nucleus PROKARYOTE = ____________ (Includes bacteria) Cell with a nucleus and organelles surrounded by EUKARYOTE membranes = _________________ (includes plants and animals) Organism that can make its own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis = ______________ AUTOTROPH Organism that gets food energy from consuming HETEROTROPH other organisms = _____________ REMEMBER A ONE-CELLED organism UNICELLULAR = _____________________ Organism made of many cells MULTICELLULAR = ______________ Polysaccharide made by joining glucose molecules together which makes plants sturdy CELLULOSE = _________________ http://bioweb.wku.edu/courses/Biol115/Wyatt/default.htm Polymer made of sugars and amino acids found outside the cell membrane in the cell PEPTIDOGLYCAN wall in some bacteria = ______________ http://www.scq.ubc.ca/?p=481 Archaea Eukarya Bacteria Eubacteria Archaebacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Figure 18-12 Key Characteristics of Kingdoms and Domains Section 18-3 Classification of Living Things DOMAIN Bacteria Archaea KINGDOM ____________ Eubacteria Archaebacteria CELL TYPE CELL STRUCTURES NUMBER OF CELLS MODE OF NUTRITION EXAMPLES Eukarya Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia DOMAIN: BACTERIA KINGDOM: EUBACTERIA PROKARYOTES _______________________ UNICELLULAR ______________________ PEPTIDOGLYCAN Have cell walls with ________________ AUTOTROPHS HETEROTROPHS Can be ____________ or ______________ E. coli, Streptococcus EXAMPLES: _____________________ http://chemiris.chem.binghamton.edu/ZHONG/research/bacteria3.jpg DOMAIN: ARCHAEA KINGDOM: ARCHAEBACTERIA PROKARYOTES _________________ _________________ UNICELLULAR Have cell walls WITHOUT peptidoglycan _________ AUTOTROPHS or ______________ HETEROTROPHS Can be ___________ EXAMPLES: _____________________ Halophiles; thermophiles; LIVE IN EXTREME ENVIRONMENTS like volcanic hot springs, brine pools, low oxygen http://www.teara.govt.nz/NR/rdonlyres/737B7002-C31D-418D-84C5-D0E68ED87BBB/134228/hero6483.jpg Organisms that can live in HIGH temperature environments THERMOPHILES = ________________ Organisms that can live in high salt environments HALOPHILES = ______________ http://web0.greatbasin.net/~wigand/petespaleo/Columbus%20Salt%20Marsh.jpg DOMAIN: EUKARYA KINGDOM: PLANTAE EUKARYOTES _______________________ MULTICELLULAR ______________________ CELLULOSE Have cell walls with ________________ and CHLOROPLASTS _____________ AUTOTROPHS _________________ Mosses, ferns, trees, EXAMPLES: _____________________ flowering plants http://www.russianflora.com/store/images/product/custom_green_plant_35.jpg DOMAIN: EUKARYA KINGDOM: ANIMALIA http://www.millan.net EUKARYOTES _______________________ MULTICELLULAR _____________________ NO CELL WALLS CHLOROPLASTS ________________ or _______________ HETEROTROPHS __________________ Worms, insects, fish, birds, EXAMPLES: _____________________ mammals, humans DOMAIN: EUKARYA KINGDOM: FUNGI EUKARYOTES _______________________ Most MULTICELLULAR; few UNICELLULAR ______________________ CHITIN Have cell walls with ________________ _______________ HETEROTROPHSabsorb nutrients from decaying __________________________________ organic matter _______________________ EXAMPLES: _____________________ Mushrooms, yeast http://www.ontarionature.org/home/images/mushrooms.jpg DOMAIN: EUKARYA KINGDOM: PROTISTA _______________________ EUKARYOTES Most UNICELLULAR; some colonial/multi ______________________ Some have cell walls with CELLULOSE ________________ Some have chloroplasts ____________________ AUTOTROPHS HETEROTROPHS Can be _____________ or _____________ Amoeba; Paramecium; EXAMPLES: _____________________ Giant kelp; slime mold http://www.ravelgrane.com/pix/proj/draco/paramecium-nahrung.gif Figure 18-12 Key Characteristics of Kingdoms and Domains Section 18-3 Classification of Living Things DOMAIN Bacteria Archaea KINGDOM ____________ Eubacteria Archaebacteria Eukarya Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote ____________ Cell walls with peptidoglycan Cell walls without peptidoglycan Cell walls of cellulose in some; some have chloroplasts Cell walls ___________ of chitin ___________ Cell walls of cellulose; chloroplasts No cell walls or chloroplasts Unicellular _____________ Unicellular Most unicellular; some colonial; some multicellular Most multicellular; some unicellular Multicellular ___________ Multicellular ____________ MODE OF NUTRITION Autotroph or heterotroph Autotroph or heterotroph Autotroph or _____________ Heterotroph _____________ Heterotroph Autotroph ___________ Heterotroph ____________ EXAMPLES Streptococcus, Escherichia coli Methanogens, halophiles Amoeba, Paramecium, slime molds, giant kelp Mushrooms, yeasts Mosses, ferns, flowering plants Sponges, worms, insects, fishes, mammals CELL TYPE CELL STRUCTURES NUMBER OF CELLS Figure 18-13 Cladogram of Six Kingdoms and Three Domains Section 18-3 DOMAIN ARCHAEA DOMAIN EUKARYA Kingdoms DOMAIN BACTERIA Eubacteria Archaebacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia