Vision - Moline High School
advertisement

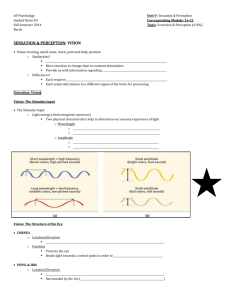
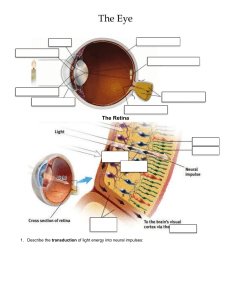
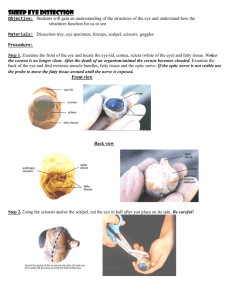
Vision Module 18 • Human’s most dominating sense • If multiple senses are competing, vision will overwhelm the others • baby The height of a wave gives us its intensity (brightness). The length of the wave gives us its hue (color). The spectrum of electromagnetic energy Video Differing Eyes Bee detects reflected ultraviolet wavelengths The Eye • Cornea – Outer transparent coating that protects the eye’s interior and focuses incoming light The Eye • Pupil – Adjustable opening in the center of the eye – Lets light in • Iris – Ring of muscle that forms the colored portion of the eye around the pupil – Controls the size of opening allowing various degrees of light in Just FYI • Blue eyes – less pigment in Iris – more susceptible to red eyes • Iris does not have enough time to close and adjust…shines to the back of the eye…showing blood vessels and tissue at the back of the eye called the retina The Eye • Lens – Transparent structure behind the pupil – Changes shape through accomodation to focus images on the retina – Cataracts are the clouding of the eye’s lens The Eye • Accommodation – Change in the curvature of the lens that enables the eye to focus on objects at various distances Vision Impairments • Myopia – Nearsightedness – Can’t see far away objects as well • Hyperopia – Farsightedness – Decreased vision for up close objects The Eye • Retina – Light-sensitive membrane at the back of the eye – Contains millions of receptors for vision – Begins the processing of visual information The Eye • Optic Nerve – Nerve that carries neural impulses to the brain • Dissection Video The Retina • Light energy rods and cones bipolar cells ganglion cells • Bipolar cells – Collect neural signals from rods and cones – Transfer messages to ganglion cells • Ganglion cells – Organize the neural signals – Axons converge into optic nerve Receptors in the Eye • Rods – Peripheral retina – Detect black, white, and gray – Twilight or low light • Cones – Near center of retina – mainly in the fovea – Fine detail and color vision – Daylight or well-lit conditions Receptors in the Human Eye Cones Rods Number 6 million 120 million Location in retina Center Periphery Sensitivity in dim light Low High Color sensitive? Yes No Vision to the brain ve then carries the neural signals to ry visual cortex sm (Ki-asm) crosses to opposite re of the brain nsferred to the thalamus where it is the visual cortex in the occipital Vision from the Eye to the Brain Visual Information Processing • Feature Detectors – David Hubel and Torsten Wiesel – Located in the visual cortex – nerve cells in the brain that respond to specific features • Shape • Angle • Movement • Sam I Am Visual Information Processing • Parallel Processing – Processing of several aspects of an object simultaneously – Crash Course