Guided Notes – Sensation & Perception – Vision
advertisement
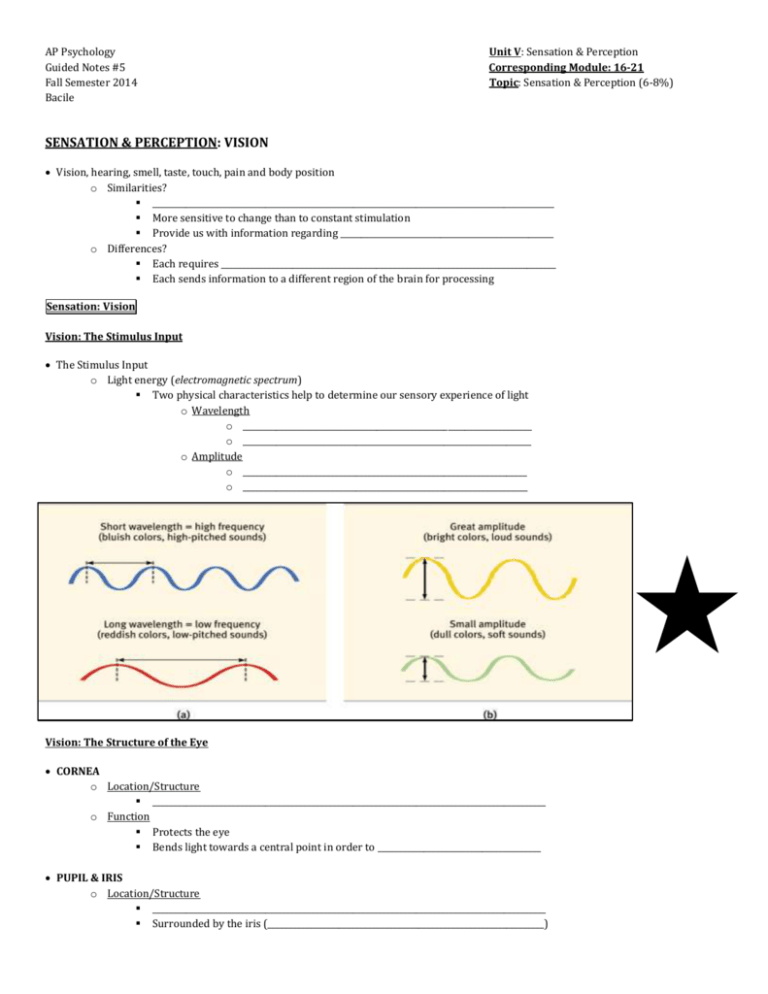
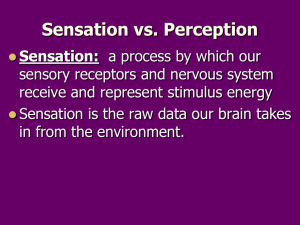
AP Psychology Guided Notes #5 Fall Semester 2014 Bacile Unit V: Sensation & Perception Corresponding Module: 16-21 Topic: Sensation & Perception (6-8%) SENSATION & PERCEPTION: VISION Vision, hearing, smell, taste, touch, pain and body position o Similarities? ________________________________________________________________________________________________ More sensitive to change than to constant stimulation Provide us with information regarding ___________________________________________________ o Differences? Each requires ________________________________________________________________________________ Each sends information to a different region of the brain for processing Sensation: Vision Vision: The Stimulus Input The Stimulus Input o Light energy (electromagnetic spectrum) Two physical characteristics help to determine our sensory experience of light o Wavelength o _____________________________________________________________________ o _____________________________________________________________________ o Amplitude o ____________________________________________________________________ o ____________________________________________________________________ Vision: The Structure of the Eye CORNEA o Location/Structure ______________________________________________________________________________________________ o Function Protects the eye Bends light towards a central point in order to _______________________________________ PUPIL & IRIS o Location/Structure ______________________________________________________________________________________________ Surrounded by the iris (__________________________________________________________________) o Function Controls the amount of light that is able to enter the eye o In ____________________________________________________ the iris __________________________, making the pupil smaller o In ____________________________________________________ the iris __________________________, making the pupil larger LENS o Location/Structure A transparent structure that is located behind the pupil o Function Focuses image on the back of the eye (retina) o Accommodation o The process by which the ___________________________________________________________________ to help focus near or far objects on the retina Lens Problems o Nearsightedness _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ Image focused in front of the retina o Farsightedness ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ Image focused behind retina RETINA o Location/Structure A multilayered, light-sensitive surface located at the back of the eyeball o Function Contains cells that ___________________________________ _________________________________________________________ Includes three layers of cells o ______________________________________________ (photoreceptors – cones & rods) o ______________________________________________ o ______________________________________________ Three Layers of Retinal Cells Photoreceptor Cells (Cones & Rods) Cones Number Location (in the retina) Color sensitive? Sensitivity in dim light? Ability to detect sharp detail (acuity)? Bipolar Cells Rods Ganglion Cells Light energy Cones & Rods Bipolar Cells Ganglion Cells OPTIC NERVE o Location/Structure ________________________________________________________________________________________ o Function Sends visual information to the thalamus and then to the occipital lobes Where the optic nerve leaves the eye, ____________________________________________________________________________________________ Vision: Visual Processing Feature Detectors o _________________________________________________________ o Nerve cells in the brain that respond to specific features ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ Parallel Processing o _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ The brain divides a visual scene into color, depth, form and movement Vision: Color Vision Young-Helmholtz Trichromatic Theory o (Hermann von Helmholtz & Thomas Young) The theory that the retina contains _______________________________________________________________________________________________ When stimulated in combination, these receptors can produce the ___________________________________________________________ o Color Blindness? Dichromatic Color Vision Individuals ________________________________________________________________; usually the red or green receptor Opponent-Process Theory o (Ewald Hering) _______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ Light that stimulates one half of the pair inhibits the other half For example, some cells are stimulated by green and inhibited by red, while others are stimulated by red and inhibited by green