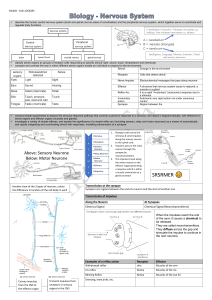
The Retina 1. Describe the transduction of light energy into neural impulses: 2. Fill in the blanks for the following parts/functions of the eye: a. The adjustable opening in the center of the eye through which light enters. ________________________________________ b. A ring of colored muscle tissue around the pupil and controls the size of the pupil opening. ________________________________________ c. The transparent structure that changes shape to help focus images on the retina. ________________________________________ d. The light-sensitive inner surface of the eye; contains rods, cones, and neurons. ________________________________________ e. The point of central focus in the retina where the cones of the eye cluster. ________________________________________ f. The point at which the optic nerve exits the eye. No receptor cells are located there. ________________________________________ g. The nerve that carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain, formed by ganglion cell axons. ________________________________________ h. Retinal receptors that detect black, white, and gray - necessary for peripheral and twilight vision. ________________________________________ i. Retinal receptors that function in daylight and detect fine detail and color. Near center of retina. ________________________________________ j. Process by which the eye’s lens changes shape to focus near or far objects on the retina. _________________________________________ k. Nerve cells in the brain that respond to specific features of the stimulus (e.g. shape, movement). ________________________________________ l. Processing many aspects of a problem or stimulus simultaneously. ________________________________________ m. Theory that retina has three types of color receptors - red, green, and blue. ________________________________________ n. Theory that visual information is processed in sets of opponent colors. ________________________________________ The Ear 1. Describe the transduction of sound energy into neural messages?