Ch 9 Covalent bonding Orbitals
advertisement

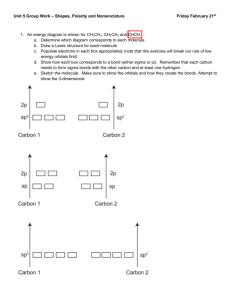
CH 9 COVALENT BONDING ORBITALS AP Chemistry 2014-2015 HYBRIDIZATION AND THE LOCALIZED ELECTRON MODEL The localized electron model (from Chapter 8) views a molecule as a collection of atoms bound together by sharing electrons between their atomic orbitals. For example, methane (CH 4 ) consists of one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms. According to the orbital diagram for carbon, there are four valence electrons—two in the 2s subshell, and two in the 2p subshell. One of the 2s electrons can get “promoted” to the 2p subshell. This move allows carbon to form four bonds, one to each hydrogen. However—this would mean that the four C-H bonds are not identical. Experimental observations show that the four C -H are identical, so this model does not correctly explain every aspect of bonding. We can modify it, though, so that carbon’s 2s and three 2p orbitals “hybridize” to form four identical sp 3 orbitals. OVERVIEW OF HYBRID ORBITALS Type of Hybridization sp sp2 Orbital Composition 1s 1p 1s 2p Number of Electron Domains Common Molecular Geometries 2 Linear 3 sp3 1s 3p 4 dsp3 (also sp3d) 1s 3p 1d 5 d2sp3 (also sp3d2) 1s 3p 2d 6 Trigonal planar Bent Tetrahedral Trigonal pyramidal Bent Trigonal bipyramidal See-saw T-shaped Linear Octahedral Square pyramidal Square planar T-shaped Linear SP HYBRIDIZATION Hybridization of one s orbital and one p orbital Two electron domains Usually occurs when an atom either a) forms double bonds to two different atoms (ex. CO 2 ) or b) forms a single bond to one atom and a triple bond to another atom (ex. HCN). One exception to this is beryllium hydride, BeH 2 . Ex. CO 2 , HCN, C 2 H 2 , N 2 , BeH 2 SP 2 HYBRIDIZATION Hybridization of one s orbital and two p orbitals Three electron domains Usually occurs when an atom forms single bonds to two atoms, and a double bond to a third atom (ex. CH 2 O). One exception to this is boron trifluoride, where boron forms single bonds with three atoms (no double bonds). Ex. C 2 H 4 , CH 2 O, BF 3 SP 3 HYBRIDIZATION Formed by the hybridization of one s orbital and three p orbitals Four electron domains Ex. CH 4 , NH 3 , H 2 O DSP 3 HYBRIDIZATION Hybridization of one s orbital, three p orbitals, and one d orbital Five electron domains Ex. PCl 5 , I 3 - D 2 SP 3 HYBRIDIZATION Hybridization of one s orbital, three p orbitals, and two d orbitals Six electron domains Ex. SF 6 FOR EACH OF THE FOLLOWING MOLECULES, WRITE THE LEWIS STRUCTURE, PREDICT THE MOLECULAR STRUCTURE, GIVE THE EXPECTED HYBRID ORBITALS ON THE CENTRAL ATOM, AND PREDICT THE OVERALL POLARITY. Molecule NF3 TeF4 Lewis Structure Molecular Structure Hybridization of Central Atom Overall Polarity Molecule KrF2 SeF6 Lewis Structure Molecular Structure Hybridization of Central Atom Overall Polarity Molecule IF3 Lewis Structure Molecular Structure Hybridization of Central Atom Overall Polarity DETERMINE THE HYBRIDIZATION OF EACH ATOM IN THE FOLLOWING MOLECULES . DETERMINE THE HYBRIDIZATION OF EACH ATOM IN THE FOLLOWING MOLECULES .