Week 1 Foundations of Economics – Production Possibilities Model
advertisement

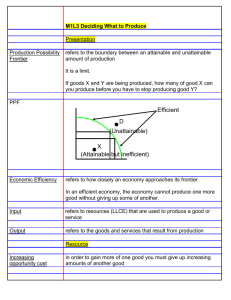
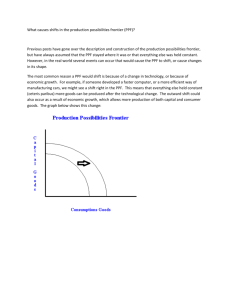
Week 1 Foundations of Economics – Production Possibilities Model - PPF The production possibilities frontier (PPF) model shows the concepts of scarcity, choice and opportunity cost. It also shows how resources can be used inefficiently. The PPF represents all combinations of the maximum amounts of two goods that can be produced by an economy given its resources and technology, when there is full employment of resources and productive efficiency. All points on the curve are known as production possibilities. Goods typically means goods AND services. For the PPF diagram, the two goods represent EVERYTHING the simple economy produces. Full employment means all resources are used; land, labour and capital. Productive efficiency means costs are at their lowest; there is no wastage (resources that are not used or excess production). Read about opportunity cost, choice and the PPF in your textbook. 1. Task. Individual work. 30 minutes. Using graph paper and a diagram that covers ½ of the page, create a PPF diagram from the following data and answer the questions that follow. Draw neatly and label the x axis “Machines” and the y axis “Food” Point to Plot A B C D E Food 40 35 26 15 0 Machines 0 17 25 31 33 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Show a point where resources are fully employed. Show a point where resources are under-employed. Show a point where production is not possible. What is the opportunity cost of moving along the curve from point B to point C? What is the opportunity cost of moving along the curve from point D to point E? What would happen if either assumption (full employment, productive efficiency) were not true? Show two points where this case might be true (one the right of the PPF and one to the left of the PPF). 7. Why might the actual, real output of the economy be inside the PPF. 2. Done this and got the T-shirt? Read ahead in your textbook: Economics as a social science. What does this mean, and what are the implications for social scientists studying production??