What are the problems with investing heavily in capital goods?
advertisement

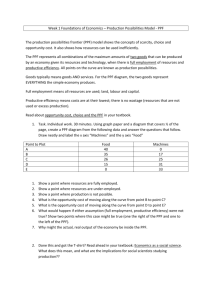
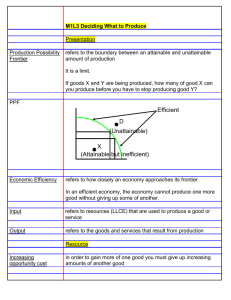
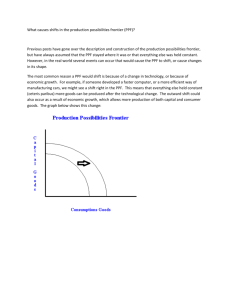
Theme 1: Introduction to markets and market failure In this theme, students will consider how markets work, looking at how supply and demand interact to allocate resources in local, national and international markets. They will learn how to apply supply and demand analysis to real-world situations and be able to offer explanations of consumer behaviour. This will involve looking at both how consumers act in a rational way to maximise utility and how firms maximise profit, but also why consumers may not behave rationally. 1.1 Nature of economics Subject content 1.1.4 Production possibility frontiers What students need to learn: a) The use of production possibility frontiers to depict: o the maximum productive potential of an economy o opportunity cost (through marginal analysis) o economic growth or decline o efficient or inefficient allocation of resources o possible and unobtainable production b) The distinction between movements along and shifts in production possibility curves, considering the possible causes for such changes c) The distinction between capital and consumer goods Objectives • To understand the reasons for shifts and movements on a PPF • To analyse the production possibility of an economy in given scenarios using diagrams • To evaluate the impact of the production of capital goods vs consumer goods Starter og onto Showbie and complete worksheet allocated to the group. Extension In the longer run, the number of resources used to make both types of goods increases in Country A. Combination B now becomes attainable and efficient. Draw another production possibility curve on Figure 2 and label it PPC2 to show this scenario. 3 70 units 80 units 7 Extension 8 What is going on here? Capital vs Consumer Goods How could a country promote growth? What could it invest in that would cause growth in the long term? Read through the article on Learning space and jot down ‘why capital investment matters’ in order to explain why in the long run capital investment is better for growth. Extension activity: Can you draw a PPF for a country that has invested heavily in capital goods? Extension thought: What are the problems with investing heavily in capital goods? Think about trade-offs/ opportunity costs. Which point do you think is the most efficient combination of resources to promote growth in an economy? Why? • What are the issues short term? What is the trade off? R Q D C P Consumer Goods A B P Capital Goods Q R Private vs Public Activity Draw a PPF. The vertical axis shows the production of public sector goods and the horizontal axis shows production of private sector goods. The economy is currently producing at Point A on the frontier where 50% of all production is devoted to public sector goods and 50% to private sector goods. a) Mark the following points on your drawing. i. Point A ii. Point B which shows production following the election of a government spending on both educations and the NHS. iii. Point C where unemployment is present in the economy iv. Point D where the government takes over production of all goods and services in the economy. b) Draw another diagram putting on it the original PPF you drew for (a), labelling it AA. i. Draw a new PPF on the diagram, labelling it PP, which shows the position after a devastating war hit the economy. ii. Draw another PPF labelling it QQ which shows an increase in productivity in the economy such that output from the same amount of resources increases by 50% in the public sector but twice that amount in the private sector. Efficiency Productive Efficiency Allocative efficiency Productive efficiency can be defined as producing goods and services for the lowest cost. All points are on the boundary are productively efficient. Allocative efficiency occurs when social welfare is maximised. There could be just one point that does this. APPLICATION APPLICATION APPLICATION