M1L3 Deciding What to Produce, Cornell Notes format
advertisement

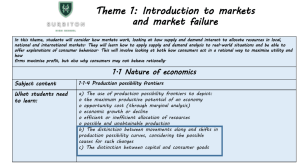
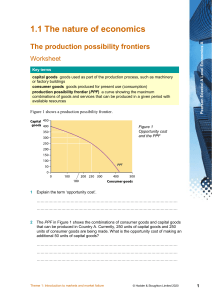
M1L3 Deciding What to Produce Presentation Production Possibility Frontier refers to the boundary between an attainable and unattainable amount of production It is a limit. If goods X and Y are being produced, how many of good X can you produce before you have to stop producing good Y? PPF Efficient D (Unattainable) X (Attainable but inefficient) Economic Efficiency refers to how closely an economy approaches its frontier. In an efficient economy, the economy cannot produce one more good without giving up some of another. Input refers to resources (LLCE) that are used to produce a good or service Output refers to the goods and services that result from production Resource Increasing opportunity cost in order to gain more of one good you must give up increasing amounts of another good Lecture Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF) a set of all combinations of goods and services that are possible in an economy given its resources and technology Aggregate goods goods that are a broad class of a type of good (a “basket” of goods) Consumption good good or service that provides immediate satisfaction for its own sake Investment goods capital; tools; goods that produce other goods, goods that are intermediary goods Investment business spending (business purchases) Production table of data for PDF Possibilities Schedule I PPS C I 0 100 100 75 50 150 50 25 170 25 0 180 0 PPF 100 75 40 80 120 160 NB. Increasing opportunity cost occurs because some resources are better suited to the production of consumption goods, while other resources are better suited to the production of investment goods C Unattainable combinations represent the reality of scarcity. Inefficient combinations represent unemployment or underemployment The downward slope represents opportunity cost Slope = rise ∆I run ∆C If any of the variables that were previously held constant (ceteris paribus) change, the whole curve must be redrawn: Example 1: Improvement in technology increases production of investment goods I bias shift C Example 2: Economic growth results from the accumulation of resources, which improves overall production I overall shift C Example 3: the effect of war – overall output would be reduced because resources are being occupied or destroyed I Example 4: overall shift C increase in immigration – overall output would increase because of increase in labor I overall shift C Example 5: an improvement in technology for consumption goods – increases the production of consumption goods I bias shift C Reading Most PPF graphs are curved, showing that the cost of choosing one option over another option increases as more resources are devoted to it. The graph curves outward to demonstrate the increasing costs. If the options have equal costs, instead of being curved, the PPF graph would be straight. Lemons 10 7 # of trees (space) 3 3 7 10 Limes