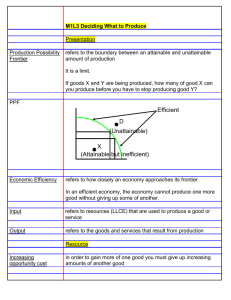
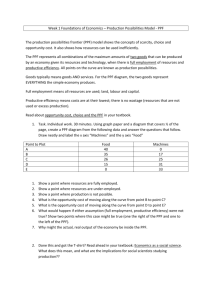
OPPORTUNITY COST AND PRODUCTION POSSIBILITY FRONTIER (PPF) TO P I C 1 : I N T R O D U C T I O N TO E C O N O M I C S THE OPPORTUNITY COST OF COVID? • What and who has been impacted as a result of diverted funds and resources that could have been used, had it not been for COVID? • What costs have emerged as a result of dealing with the global pandemic? THE OPPORTUNITY COST OF COVID-19 OPPORTUNITY COST AND PPF • The cost of alternative uses in economics is known as opportunity cost. • Opportunity cost may be expressed in terms of: money, time and items forgone. • Opportunity cost is best illustrated through the PPF or curve. THE PPF MODEL • Assumptions underlying the PPF model: - Only 2 goods are being produced. - All resources are fully employed and fixed. - Resources are fixed but can be switched from one type of production. - Technology remains constant PPF CURVE MOVEMENTS ALONG THE PPF UNATTAINABLE POINTS OF PRODUCTION SHIFT OUTWARD PPF COMPARATIVE ADVANTAGE • An economy may be able to produce for itself all of the goods and services it needs to function using the PPF as a guide. However, this may actually lead to an overall inefficient allocation of resources and hinder future growth when the benefits of trade are considered. • Through specialisation, a country can concentrate on the production of just a few things that it can do best, rather than trying to do everything on its own. • Comparative advantage is based on the opportunity cost of producing a good. If a Country can produce a particular good at a lower opportunity cost than any other country then it is said to have a comparative advantage. • What areas does Australia hold a comparative advantage in? • In other words, what goods or services can Australia produce better than another country using the same amount of resources?