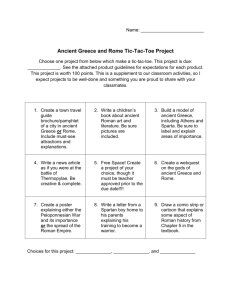
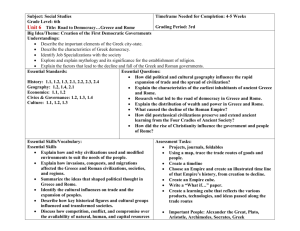
3rd Grade Social Studies Unit Plan – Day 1
advertisement

Cairn Jones TEDU 330 LESSON GOALS – DAY 1 (LOCATION, GOODS & SERVICES) Grade 3: Introduction to History and Social Science ANCIENT GREECE & ROME Main Idea: Location, Goods & Services The standards for third-grade students include an introduction to the heritage and contributions of the peoples of ancient Greece and Rome. Students should continue developing map skills and demonstrate an understanding of basic economic concepts. Students will explain the importance of the basic principles of democracy and will identify the contributions of selected individuals. Geography 3.4 The student will develop map skills by a) Locating Greece and Rome b) Describing the physical and human characteristics of Greece and Rome c) Explaining how the people of Greece and Rome adapted to and/or changed their environment to meet their needs. Economics 3.7 The student will explain how producers in ancient Greece and Rome used natural resources, human resources, and capital resources in the production of goods and services. 3.8 The student will recognize that because people and regions cannot produce everything they want, they specialize in what they do best and trade for the rest. ("Standards of learning") Cairn Jones TEDU 330 LESSON GOALS – DAY 1 (LOCATION, GOODS & SERVICES) Location and how it affected the goods and services of each region Identifying location of Ancient Greece and Rome on a map Specialization and the beginning of trade Advantages in locations of each city-state Natural resources produced Natural, Human, Capital Resources Goods and services originating in including Greece/Rome 1. What benefits did Ancient Greece and Rome experience due to their location? What were the downsides to the location? 2. What impact did some of these resources have on the goods and services produced in these areas? 3. Which goods and services did each city-state specialize in? 4. What services did the Romans specialize in? Did these services have anything to do with the location of the empire? Cairn Jones TEDU 330 LESSON GOALS – DAY 1 (LOCATION, GOODS & SERVICES) The students will begin the unit on Ancient Greece and Rome, first by learning where each place is located on a map and then being able to identify each location themselves. These students will master the locations by learning the quick tips associated with recognizing each country. After each student is able to identify locations, they will be able to efficiently associate natural resources and their origins, as well as where they are in relation to one another. After learning about natural resources, the students will move onto human and capital resources and the beginning of goods and services being developed, as well as what specialization is. They well be able to associate this concept of economics with that of modern society. The Evidence Based Practices used in each lesson are italicized. Assessments are included throughout the unit plan and are in bold. PBIS: Each of these lessons will use the PBIS elements (define, teach, and remind) to ensure that all students are clear on the concept before moving onto the next, good behavior will also be praised as it is exhibited to encourage more of the same behavior, instead of punishing the negative. During this unit, the children will be taught and encouraged to master the behaviors of silence when appropriate and raising their hands when they have a question, so that they learn to speak in turn. Each student who exhibits any of these behaviors will be verbally praised and recognized by the teacher, and encouraged to continue this behavior. The classroom will go by a point system, in which the instructor will give add a marble to a jar in the front of the classroom each time they earn a point. Points will be earned each time they exhibit this behavior, as well as each time a child exhibits a positive behavior as an individual. Each time any student exhibits a positive behavior (helping without being asked, being kind, volunteering services) the student will be allowed to place a marble in the jar. Throughout the course of the school year, the size of the jar will change periodically (ex. Small to medium sized Mason Jars) to vary amount of time it takes to earn each reward. This will encourage each student to be on their best behavior and be good to one another. Each time the jar fills up, the class will vote on their reward (pizza party, movie day, etc.). Cairn Jones TEDU 330 LESSON GOALS – DAY 1 (LOCATION, GOODS & SERVICES) Modifications are included within the unit plan for four children in the classroom who have ADHD, Autism, EBD, Visual impairment. Each of these students will have individual progress reports in their classroom folders, any personalized positive behavior or compliments received during or outside the classroom will be recognized throughout the course of the day with a sticker so that the child can track their own progress. If they fill out their progress report with less than 5/20 blank spots each week, they will receive a small prize. o o o o The child with ADHD is a boy who has difficulty remaining in his seat, staying concentrated on tasks, and calling out answers out of turn. Specific behaviors to be rewarded for: staying on task, speaking in turn, sitting still, participation in classroom activities. The child with ASD is a girl is very high-functioning, but sometimes has trouble understanding concepts and staying on task. Specific behaviors to be rewarded for: positive social interactions with other students, remaining focused, participation in classroom. The child with EBD is a boy who uses offensive language and exhibits aggressive behavior, behaves inappropriately toward others. Specific behaviors to be rewarded for: using words instead of acting out, keeping hands to self, positive social interactions in group settings, participation in classroom activities. The child with Visual Impairment has limited vision due to a previous trauma, this child is nearsighted and needs extra time to complete activities. Specific behaviors to be rewarded for: participation in classroom activities. Vocabulary in section: Natural resources, human resources, capital resources, goods, services, producers Learning Log: The students will begin the day by writing in their journals about what they already know regarding the geographical location of each city-state. They will also write about what they think the definition of goods/services is, as well as what they perceive to be a good or service that they use every day. A map of the region will be displayed in the front of the classroom for each student to use as a reference, if needed. If the child struggles writing, they may draw a picture/cartoon or use the computer to type up their responses if that facilitates things for them. The students will also be able to write any questions they may have; these journals will be reviewed each day by the teacher and this will allow the questions to be answered or explained on a more personal level. (Children with ADHD, EBD, ASD and VI will receive modified handout with picture prompts, child with VI will also be issued a printed out copy of the map for reference.) Cairn Jones TEDU 330 LESSON GOALS – DAY 1 (LOCATION, GOODS & SERVICES) Geography: - 1) After having a class discussion in which the students are asked to name examples of any items they may know which are associated to each location (i.e. Italy – pizza, Greece – birthplace of Olympics). The students will then receive and individually locate Ancient Greece and Rome on a map handout and be instructed to color and label each location independently; this will be modeled by the teacher with a large map up on the board, as an example, with both locations labeled. One trick that the children will learn to help them recognize Italy is that it is the shape of a boot, and Greece is the other peninsula to the East of Italy. - 2) The students will learn about the natural resources and where they originate, and what influence the location may have on these resources. This will be learned through an interactive PowerPoint lecture with guided notes for the students follow along with and complete throughout the lecture. Highlighted text clarifies importance of certain resources to each city-state. (Child with VI will receive completed copy so they can follow along at their own pace). Natural resources: o Greece – located on peninsula: many islands, mountains and hills; surrounded by Mediterranean sea, fishing; limited rich soil Resources provided: natural shelter from attack of enemies (water, mountains) [use Great Wall of China as example of protection – relate to mountains] fish [fishing and farming important – feeds community, helps it grow] o Rome – located next to river, fishing; limited rich soil; many hills, lots of trees Resources provided: land out of flood range [good for farming – reliable soil that would not wash out crops] farming communities provided lots of work sea access through river [allowed for fishing as well] The students will then complete a vocabulary activity having to do with natural resources, which will allow them to make visual connections of these goods to their place of origin. This activity will be a flashcard game that the students will complete in pairs, these flash cards will have an image on one side and the students must guess the vocabulary word pertaining to the image. They will then be asked to group each object into which location they originate in. (Student with VI will benefit from this activity, because the visuals on the card will allow them to relate them to the vocabulary word on the other side. Student will also receive flash cards with larger text to assist them in this game with partner). Cairn Jones TEDU 330 LESSON GOALS – DAY 1 (LOCATION, GOODS & SERVICES) Geography Goods & Services Goods & Services: 1) The students will participate in a class lecture about the natural/human/capital resources from each location. In this lecture, the students will learn: Natural resources: o Greece – located on peninsula: many islands, mountains and hills; surrounded by Mediterranean sea, fishing; limited rich soil o Rome – located next to river, fishing; limited rich soil; many hills, lots of trees Human resources: o Greece – farmers/fishers, shipbuilders, traders o Rome – farmers/fishers, road builders, traders Capital resources: o Greece – built ships, used for trading o Rome – built roads; ships for trading This lecture will be demonstrated with an interactive PowerPoint, containing practice questions via the Clicker system and will contain many visual supports, including maps and images of certain resources. The students will then individually participate in quiz via polling website www.polleverywhere.com, so teacher can view each student’s progress and response. (Child with ADHD will maintain interest and attention span by being actively engaged by the Clicker prompts as well as the competitive game format). (Child with VI will receive paper copy of PowerPoint lecture to review along with the presentation, and will respond to Clicker questions when questions are read aloud by teacher). Sample of polling questions: What human resources did both city-states have in common? Which empire has many islands and was surrounded by the Mediterranean Sea? Which empire built roads? What are two examples of natural resources? Each question will be multiple choice and will contain visuals if they are applicable. Cairn Jones TEDU 330 LESSON GOALS – DAY 1 (LOCATION, GOODS & SERVICES) - 2) After watching a short video entitled “Producers & Consumers…Goods & Services 2nd Grade” available on YouTube, (video will be slowed down and teacher will read subtitles out loud to ensure that students have multiple means of receiving information) in which the students learn the definition of producers: people who use resources to make goods and or/provide services; goods: things that people make or use to satisfy needs and wants; services: activities that satisfy people’s needs and wants. This video will be accompanied with guided notes, so the students are required to follow along with the video and fill in the blanks. The students will then move freely to three different stations of blank banners and art supplies established throughout the classroom, where they will express creativity by creating an example(s) of a good (can be any item they want/use/need), a service, and an example(s) of a producer they may know (Lego, Pillsbury, etc.) Teacher will actively supervise this activity to ensure that it goes smoothly, and to be able to perform precorrections to possible negative behaviors. (Child with ASD and ADHD will benefit from the physical movement and creative stimulation this activity has to offer). - 3) The students will learn participate in a short PowerPoint lecture about the importance of specialization for each location and how it impacted the culture of the Ancient Greeks and Romans. Students will be split into pairs and create an advertisement for any good/service/resource either Greece or Rome specialized in. This activity can be done by drawing/painting on a poster, using a computer to design a pamphlet, using art supplies to make a model. (Child with EBD will be paired with a friend to encourage this child to exhibit good behavior while completing an activity designed to be fun and stimulating). Daily Wrap-Up: The students will participate in a class discussion (groups of 3), discussing the relevancy of trade and specialization then and now. The students will offer their own ideas of things they believe we consider the most common goods & services in the U.S today and what goods or services the children use the most. This will allow them to be independent thinkers while making new connections/associations for themselves. (Child with ADHD and child with ASD will to do this activity on a computer using a program that simulates a game in which they find objects we use most often today). Cairn Jones TEDU 330 LESSON GOALS – DAY 1 (LOCATION, GOODS & SERVICES) Work Cited: Producers & consumers..goods & services [Web]. Retrieved from http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fxfbvQsCeTE Standards of learning documents for history & social science. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.doe.virginia.gov/testing/sol/standards_docs/history_socialscience/index.shtml