How to read skeletal x-ray
advertisement

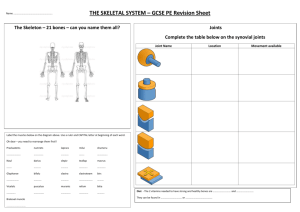
HOW TO READ SKELETAL X-RAY Dr. Suheab Maghrabi MBBS, MSc. • X rays: Electromagnetic Radiation. • Absorption varies between tissues. • Bone • Soft tissue • Air • Be systematic. • Don’t rush to conclusions. • Common rules: 1. Two views. At 90 degrees, usually anterior-posterior and lateral. 2. Two joints. The joints above and below. 3. Two occasions. Some fractures are not easily visible immediately after trauma. 4. Two limbs. If required for comparison. 1. Patient profile. 2. Orientation. 3. Bone. 4. Joint. 5. Soft tissue. • Patient profile • Name. • Date • Adequacy (penetration, joint A/B) • Orientation • View (AP, L or special view). • Side (R/L) • Bone (which bone?). • Joint. • Bone: • Deformity. • Fracture: • Location • Pattern • Deformity (distal in relation to proximal). • Displacement • Angulation • Rotation • Density. • Radio-Lucent/Opaque. • Joint: • Dislocation. • Fracture. • Degeneration. • Soft tissue: • Swelling • Calcification Thank You