Ratio Analysis of Accounts
advertisement

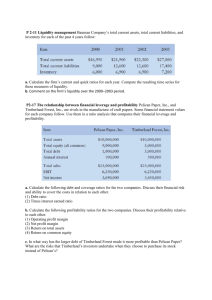
Ratio Analysis of Accounts Lesson Objectives for Today: • Differentiate between profitability & liquidity ratios. • Calculate the main financial Ratios. • Analyze the main financial ratios. Why do businesses use Financial ratios? • We can monitor the performance of the company • We can measure the financial strength of the company Liquidity • The degree to which an asset or security can be bought or sold in the market without affecting the asset's price. Liquidity is characterized by a high level of trading activity. Assets that can be easily bought or sold are known as liquid assets. • The ability to convert an asset to cash quickly. Also known as "marketability.“ • There is no specific liquidity formula; however, liquidity is often calculated by using liquidity ratios. http://www.investopedia.com/video/play/liquidity/ Ratios you need to know how to calculate: • ROCE (Return on Capital Employed) • Gross Profit Margin • Net Profit Margin • Current Ratio • Acid Test Ratio Return On Capital Employed (ROCE) ROCE (%) = Operating Profit x 100 Capital Employed What does it show? • The ROCE is considered to be the best measure of profitability. The ROCE indicates how much money is made by the business, compared to how much money has been ‘put into’ the business. • A decent ROCE would range from 20 – 30%, however, again this ratio is industry specific. Gross Profit Margin Gross Profit Margin (%) = Gross Profit x 100 Sales Turnover What does it show? • The GPM tells us the profit a business makes on its cost of sales, or cost of goods sold. • Gross profit is the profit we earn before we take off any administration costs, selling costs and so on. • The ratio can be improved by increasing prices or reducing the direct cost of sales. Net Profit Margin Net Profit Margin (%) = Net profit before tax x 100 Sales Turnover What does it show? • The net profit margin ratio tells us the amount of net profit per £1 of turnover a business has earned. That is, after taking account of the cost of sales, the administration costs, the selling and distributions costs and all other costs, the net profit is the profit that is left, out of which they will pay interest, tax, dividends and so on. • NPM can be improved by raising prices or lowering cost of sales or expenses. Current Ratio Current Ratio = Current Assets Current Liabilities What does it show? • The current ratio should be higher than 1:1; however, 1.5:1 – 2:1 is considered as ideal. This represents £1.50 or £2 of current assets to every £1 of current liabilities. • A value of below 1.5:1 suggests a liquidity/solvency problem. • A current ratio in excess of 2:1 may indicate poor management of resources with capital tied up in stocks, debtors or lying idle in the bank. Acid Test Ratio Acid Test Ratio = Current assets – stocks Current Liabilities What does it show? • Stock is the least liquid of current assets. It has to be sold first, turned into debtors and then eventually into cash. • A ratio of 1:1 is generally considered as satisfactory. This represents £1 of liquid assets to every £1 of current liabilities – showing both amounts are the same. • A value of below 1:1 suggests a liquidity/solvency problem. The business does not have enough current assets to meet short term liabilities, for example, creditors. Individual Activity Calculate the following ratios: • ROCE (Return on Capital Employed) • Gross Profit Margin • Net Profit Margin • Current Ratio • Acid Test Ratio Extension Comment on what each result shows and how might they act on the result. Profit and Loss 2005 ($000) Sales Turnover 1,250 Cost of Sales 900 Gross Profit 350 Operating Expenses 105 Operating Profit 245 Interest Payable 50 Profit before Tax (Net Profit) 195 Corporation Tax 35 Profit after Tax 160 Dividends 120 Retained Profit for the year 40 Review ROCE = = 245 x 100 1,160 21 .1% The higher the result the more successful are the managers in earning profit from capital used in the business. Review Gross Profit Margin = 350 x 100 1,250 = 28% This means that on every $ worth of goods sold, the company made on average 28 cents gross profit. Review Net Profit Margin = 195x 100 1,250 = 15.6% The higher this result, the more successful the managers are in making profit from sales. Review Current Ratio = 140 130 = 1.1:1 This result is low. It means the business could only just pay off its short term debts from current assets. A safer ratio would be between 1.5 - 2 Review Acid Test Ratio = 140 – 80 130 = 0.46:1 This is low. A result of 1 would mean the company could just pay off its debts. This result means that the company cannot afford to do this.