Genitourinary System - Medical Assistant Program
advertisement
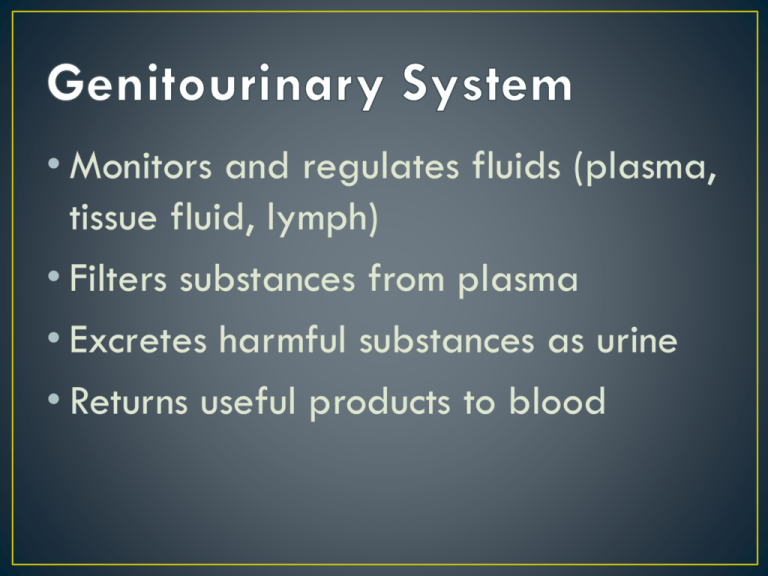
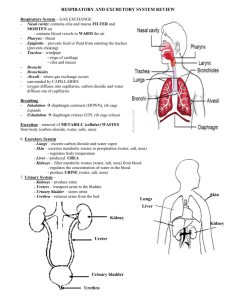
• Monitors and regulates fluids (plasma, tissue fluid, lymph) • Filters substances from plasma • Excretes harmful substances as urine • Returns useful products to blood • Macroscopic • Kidneys • Renal Artery • Renal Vein • Renal Pelvis • Ureter • Urethra • Urinary Meatus • Kidney: fist sized, kidney shaped organs that filter tissue fluids and reabsorb useful nutrients for the body • Renal Artery: carries blood containing waste to kidney • Renal Vein: carries “cleaned” blood out of kidney • Renal Pelvis: waste material in the form of urine stored here during filtering process • Ureter: extends from renal pelvis and carries urine to bladder • Bladder: temporary reservoir for urine • Urethra: tube at base of bladder that releases urine • Urinary Meatus: urine expelled; in females, located above the vagina Structural overview • The most common disorder of the urinary system • UTI is a broad diagnosis covering any infection of the urinary tract including the urethra, ureters, bladder and kidneys. • May be caused by virus or fungus; most common infection is caused by bacteria • • • • • • • Dysuria – painful urination Proteinuria – protein in the urine Hematuria – blood in the urine Pyuria – pus in the urine Oliguria – absence of urine production Frequency, urgency Flank/back pain, fever, nausea, vomiting • Cystitis is the medical term for inflammation of the bladder which is the most common area of infection • Diagnostics: U/A – urinalysis, C&S – culture and sensitivity, blood tests (BUN, CBC, Electrolytes), IVP – intravenous pyelogram, Cystoscopy, Biopsy • Treatments: based on cause. Antibiotics, catheterization, surgery, dialysis, lithotripsy, anti-hypertensive medications