Urinary System - Dr. Halbert's Wiki Site!!!!
advertisement
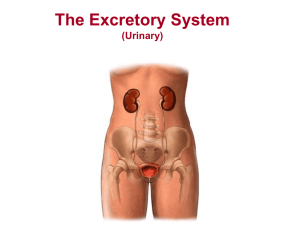
Urinary System Health Science Technology Dr. Halbert Urinary system = excretory system Removes some wastes & excess water and maintains pH balance Consists of 2 kidneys, 2 ureters, bladder and urethra Kidney On either side of vertebral column separated from the abdominal cavity by peritoneum Enclosed in a mass of fatty tissue called adipose capsule Also covered by tough fibrous tissue called renal fascia or fibrous capsule Kidney structure 2 main sections Cortex Medulla Cortex: outer section, contains most of the nephrons Medulla: inner section, contains most of the collecting tubules, which carry the urine from the nephrons thru the kidney Hilum Notched or indented area of the kidney thru which ureter, blood vessels & lymph vessels enter & leave kidney Nephron Filtering unit of kidney One million nephrons per kidney Consists of Glomerulus Bowman’s capsule Proximal convoluted tubule Distal convoluted tubule Collecting duct Glomerulus First part of nephron Cluster of capillaries As blood passes thru from renal artery, water, mineral salts, sugar are filtered out of blood RBCs & proteins are not filtered out Filtered blood makes its way to renal vein Bowman’s capsule C-shaped structure that surrounds the glomerulus & is start of convoluted tubule Picks up filtered material from glomerulus & passes them to convoluted tubule Passing through tubules Substances needed by body are reabsorbed & returned to blood capillaries Excess sugar, mineral salts; some water; & wastes remain in tubule & become urine Urine enters collecting ducts located in medulla Renal Pelvis Collecting ducts empty into renal pelvis, funnelshaped structure which is first section of ureter Ureters Two muscular tubes About 10-12 inches Peristalsis moves urine through the ureter to the bladder Bladder Hollow muscular sac that lies behind the symphysis pubis & at midline of pelvic cavity Mucous membrane lining arranged in folds, rugae which disappear as bladder expands with urine Bladder wall Formed by three layers of smooth muscle Bladder stores urine until eliminated Urge to void occurs when bladder contains 250 cc (1 cup) of urine but bladder can hold much more Sphincter Circular muscle controls opening of bladder to prevent emptying Urethra Tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside External opening is the urinary meatus Urethra Male vs Female Female 3.75 cm (1½ in) Carries only urine Opens in front of vagina Male 20 cm (8 in) Carries urine & semen Passes through prostate & out through penis Urine Liquid waste product produced by urinary system 95% water Waste products: urea (major waste product), uric acid, creatinine, mineral salts, pigments Urochrome: pigment giving urine its yellow color About 1½ to 2 quarts produced daily from 150 quarts of liquid that is filtered through the kidney Terms Polyuria: excessive urination Oliguria: decreased amounts of urine Anuria: absence of urine Hematuria: blood in urine Pyuria: pus in urine Nocturia: urination at night Dysuria: difficult or painful urination Retention: inability to empty the bladder Incontinence: involuntary urination Diseases of Urinary System Cystitis Inflammation of the bladder Usually caused by pathogens entering urinary meatus More common in females Glomerulonephritis Inflammation of the glomerulus Acute form: usually follows a streptococcal infection Chronic form: progressive disease that causes scarring of the glomeruli leads to kidney failure Pyelonephritis Inflammation of kidney tissue & renal pelvis usually caused by bacteria Renal calculus Kidney stone Calculus is formed when salts in the urine precipitate May become lodged in renal pelvis or ureter Renal failure When kidneys stop functioning Acute renal failure (ARF): caused by hemorrhage, shock, poisoning, injury, dehydration Chronic renal failure (CRF): results from progressive loss of kidney function, caused by hypertension, toxins, endocrine disease, chronic glomerulonephritis Uremia Toxic condition that occurs when kidneys fail & waste products are present in blood stream Urethritis Inflammation of the urethra usually caused by bacteria, viruses or chemicals Image Citations Slide 3: Anatomy of the urinary system, front view, 1/1/07, http://www.health.uab.edu/default.aspx?pid=65499 Slide 5: Illustration of the anatomy of the kidney, 1/1/07, http://www.uchospitals.edu/online-library/content=P01468 Slide 8: Glomerulus, 2/17/07, http://www.aic.cuhk.edu.hk/web8/Hi%20res/Glomerulus.jp g Slide 13: Male Bladder & urethra, 2/17/07, http://www.ivyrose.co.uk/Topics/Urinary/Bladder_Urethra_Female_cIvyRo se.jpg Slide 18: Urine, 2/17/07, http://www.open2.net/open2static/source/file/root/32/15/1 32078/urine.jpg Slide 21: Cystitis, 2/17/07, http://www.pathology.vcu.edu/education/renal/lab2.p.html