study guide for test 2!!!!
advertisement

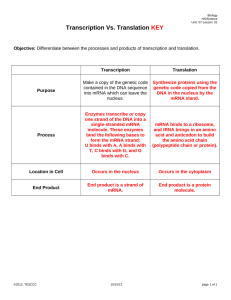
Cellular Metabolism Study Guide www.elmwoodbiology2.weebly.com To study for this test: Read chapter 4 in your textbook, as well as any additional readings provided Enzymes Cellular Respiration Translation Review all quizzes!! Review videos, animations, or articles on the class website for extra help Review any homework assignments and labs Review all your notes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. What are enzymes? How do they work to speed up biological reactions? What macromolecule is an enzyme? What is the lock and key model? Reconize what a substrate, enzyme, and active site is How do competitive inhibitors work? How can an enzyme catalyzed reaction be altered (sped up or slowed down) Define metabolism Know the difference between anabolic and catabolic Know the difference between hydrolysis and dehydration synthesis (which one splits water and which one loses water) 10. What is cellular respiration? 11. What happens to the original carbon in glucose in cellular respiration? 12. What does cyanide do? 13. What is the main goal of the Kreb’s cycle? 14. What is the main goal of the ETC? 15. How does ATP release energy? Draw this 16. Be able to describe the structure of DNA 17. What is the complementary base pairing rule 18. What are the bonds between DNA’s backbone? What are the bonds between the nitrogen bases? 19. Describe how DNA replication occurs, and be able to label the enzymes involved 20. Differentiate between the leading and lagging strand in DNA replication 21. What is transcription 22. Describe the 4 steps of transcription and the major players in each step 23. Be able to transcribe a single DNA strand into its corresponding mRNA strand (which base is different) 24. What is translation 25. Be able to label the enzymes and parts involved in translation (look at your 6 questions you answered here!) 26. What is PCR and when is it used 27. How does tRNA work? What are codons and anticodons? 28. Use the codon chart to translate an mRNA into amino acid sequence 29. Know the different types of mutations and the effects they can have on the protein 30. How much of human DNA actually codes for proteins