Synovial joints - churchillcollegebiblio
advertisement

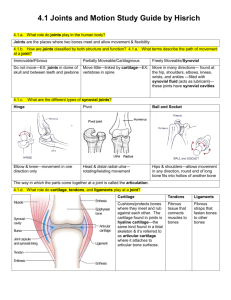
SYNOVIAL JOINTS What are they?! Skeletal System Skeletal System Features of a synovial joint include: Articular capsule joint capsule; the saclike envelope enclosing the cavity of a synovial joint. Articular cartilage reduce friction and absorb shock. Synovial membrane the inner layer of the capsule which secretes synovial fluid Synovial fluid a lubricating liquid Bursae a small fluid-filled sac situated in places in tissues where friction would otherwise occur. Meniscus A disk of cartilage that acts as a cushion between the ends of bones in a joint. Skeletal System The 6 types of synovial joint are: Ball and socket Hinge Pivot Gliding Condyloid (ellisoid) Saddle synovial joint types Hinge Joint This allows movement in one plane only : UNIAXIAL Examples: Knee Joint used extensively in sport. Arm Joint Pivot Joint This allows rotation only and is therefore also uniaxial. Examples: Axis and atlas bones of cervical vertebrae Ellipsoid Joint This is biaxial, allowing movement in two planes Examples: Radiocarpal joint of the wrist Gliding Joint This is when two flat surfaces glide over one another and can permit movement in most directions, although mainly biaxial. Examples: Carpel Bones in the Wrist Saddle Joint This is when a concave surface meets a convex surface and is biaxial. Examples: Carpalmetacarpal joint of the thumb. Ball and Socket Joint This allows a wide range of movement and occurs when a round head of bone fits into a cup-shaped depression. Examples: Shoulder joint What holds our bones at a joint? • LIGAMENTS! • These are bands of c……………. t…………. between bones. They prevent extreme movement and d…………………. • They are very tough and help join bones together and keep them stable. • Some form the s…………… c…………… while others are outside the capsule. Why don’t our bones bang together?! • CARTLIAGE! • This is soft connective tissue. • Cartilage has no b………… supply but receives nutrition through diffusion from the surrounding c……………… network. • There are three types of cartliage.. • Yellow, hyaline/blue articular and white fibro Articulating bones • These are the bones present at a synovial joint that allow the m………………… to take place. • An example in the shoulder joint would be… • Which is what type of joint? How does a healthy lifestyle effect a performers joints? • How does a HAL benefit joints? • Short and long term benefits • Movement = secretion of s……………… fluid which • • • • increases the r…… of movement at a joint Long term increase in flexibility Increase bone st............... and c……………. and phosphate Thicker h…………….. cartilage Greater stretch potential of ligaments PRACTICAL EXAMPLES • Think of a practical example for each of the Synovial Joints. • Hinge • Pivot • Ellipsoid • Gliding • Saddle • Ball + Socket Sprinting Turning head in Hockey Forehand clear in Badminton Dribbling the ball in Hockey Gripping tennis racket with thumb Athlete throwing a Javelin Table teasers.. • In your tables, come up with a multiple choice question about something that you have learnt today or during the past couple of lessons. • You will then choose a table to question and see if they can get the correct answer.