Articulation Quiz Spring 2000.
advertisement

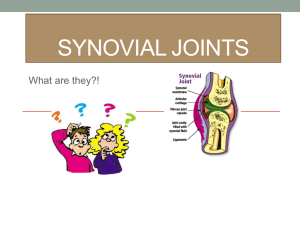
NAME_______________________ BIOLOGY 2401 DATE_______________________ ARTICULATIONS S2000 1. What are the functions of the below structures? a. ligaments – b. menisci – c. synovial membrane – 2. List all the motions possible with the below joints. a. between the radius and scaphoid bone – b. between the first humerus and ulna – 3. List one function for the below structures. a. articular cartilage – b. bursae 4. A joint that does not move is known as a/an synarthrosis/amphiarthrosis/diarthrosis. A freely moveable joint is known as a/an synarthrosis/amphiarthrosis/diarthrosis. 5. A joint held together by collagen with no joint cavity would be classified struturally as a fibrous/synovial/cartilaginous joint. A joint with a joint cavity in which the bones are heled together with an articular capsule and ligaments would be structurally classified as a fibrous/synovial/cartilaginous joint. 6. Where would you find the below structures? a. rotator cuff – b. anterior cruciate ligament – c. gomphosis – 7. Turning the palms anteriorly is a specialized form of rotation known as ____________. Closing your mouth is known as ___________________. 8. Pointing the foot and toes up is known as _________________. Shaking your head no is known as __________________. 9. Bending backward at the waist is a movement known as _________________. Moving your thighs apart is known as ___________________. 10. Identify the below synovial joint types. a. Between the trapezium and first metacarpal. __________________ b. Between the sternum and clavicle. ___________________ c. Between the proximal radius and ulna. __________________ d. Between the mandible and temporal bone. _________________ e. Between the tibia and femur. __________________ f. Between the humerus and scapula bone. ___________________ g. Between the proximal and middle phalanges. _______________ 11. List the factors that limit the range of motion of a joint. 12. List all the different types of synovial joints that you have in your hand. 13. Describe the below conditions. a. patellofemoral stress syndrome – b. rotator cuff injury – c. a sprain – d. a strain – e. bursitis – f. rheumatoid arthritis – g. osteoarthritis -