Chapter_13_Answers
advertisement

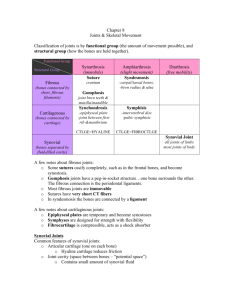
Chapter 13 Answers Review Questions 1. 2. a. The region where two or more bones meet. b. Size and shape of bones Ligaments (join bone to bone) Tendons (join muscle to bone) Muscles Injuries Disease Age Cartilage Exercise/fitness a. Fibrous – bones are fused together, no movement. b. Cartilaginous – bones separated by cartilage, some movement. c. Synovial- bones separated by synovial tissues, freely movable. 3. a. Flexion b. Extension c. Rotation d. (circumduction) e. Abduction f. Adduction 4. Type Ball and socket Movement ab, ad, rot, circ Examples Shoulder Hip Hinge Fl, ex Elbow Knee Picture Pivot rot Atlas/axis Radius/ulna Gliding Fl, ex, ab, ad Scapula/ribs Sternum/clavicle Carpals Tarsals Saddle Fl, ex, rot Thumb 5. Synovial Joint Bones Ligament Synovial Capsule Synovial membrane Synovial fluid Articular cartilage Bursae Meniscus 6. a. Fibrous synovial capsule, accessory ligaments b. Hold the joint together (see diagram). Connective tissue. Apply Your Knowledge 3. femur – articulate with tibia tibia – articulate with femur patella – provide surface area for muscle attachment. accessory ligaments – hold bones together cruciate ligament – hold bones together articular cartilage – help reduce friction meniscus – divide the synovial cavity synovial capsule – hold the synovial membranes and fluid around the joint. synovial membrane – produce synovial fluid. Bursae – lubricate joint. 4. Reduces friction and absorbs shock. Without it, joints would not function. Bone would wear away. Articular cartilage is not ‘slippery’ enough. Also provides nourishment to articular cartilage. 5. Muscles & tendons Accessory ligaments Cruciate ligaments (knee only) Synovial capsule Synovial membrane (lesser extent)