Arthrology: Study of Joints - Types, Structure, & Function
advertisement

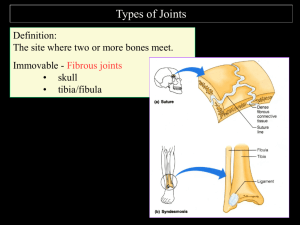
Arthrology Arthrology Definition: • Greek, (arthro= joint), (logos= science). • Arthrology is study of joints Joints • Joints are places where two or more bones are connected Classification Based on Structure 1. Non movable 2. Semi-moveable 3. movable. Non Moveable Joints • • Bones connected by fibrous tissue No joint cavity a) Skull b) Fibula - Tibia Skull (Sutures) Tibia – Fibula (Syndesmoses) Semi moveable joints - The bones are connected by cartilage There is no joint cavity A. Ribcage B. In between Vertebrae Ribcage In between Vertebrae Cartilage • Soft bone • Found in ear, nose and joints Synovial Joints • • • • Most movable joints in the body There is a joint cavity. Cartilage covers the ends of the opposing bones) Ligaments keep bones together Synovial joint Arthritis Types of Moveable Joints 1. Ball and Socket Joint Allow for the most freedom of movement Types of Moveable Joints 2. Hinge joint allows movement in only one direction. Back and forth Types of Joints 3. Pivot joint – Allows rotation Types of Joints 4. Saddle joint - Thumb Types of Moveable Joints 5. Condyloid joint One bone is slightly rounded and fits in the other one Types of Moveable Joints 6. Sliding or gliding joint - Two flat surfaces that slide over each other Types of Joints Joint Type Ball and Socket Hinge Saddle Pivot Condyloid Gliding Example Basic Structure & General Anatomy • Articular capsule encloses joint cavity – continuous with periosteum – lined by synovial membrane • Synovial fluid = slippery fluid; feeds cartilages • Articular cartilage = hyaline cartilage covering the joint surfaces • Articular discs and menisci – jaw, wrist, sternoclavicular and knee joints – absorbs shock, guides bone movements and distributes forces • Tendon attaches muscle to bone • Ligament attaches bone to bone Tendon Sheaths and Bursae • Bursa = saclike extension of joint capsule – between nearby structures so slide more easily past each other • Tendon sheaths = cylinders of connective tissue lined with synovial membrane and wrapped around a tendon Bursae and Tendon Sheaths Classification Based on Function • Synarthroses-immovable joints (sutures) • Amphiarthroses- slightly movable joints( fibrous connection)( intervetebral discs) • Diarthroses-freely movable joints( synovial) • Synarthroses and amphiarthroses are largely restricted to the axial skeleton • Diarthroses predominate in the limbs. Summary of Joint Classification Structural Class Fibrous Cartilaginous Characteristics Bones united by collagen fibers Bone ends united by cartilage Types 1. 2. 3. 1. 2. Synovial Bone ends covered with articular cartilage and enclosed within a capsule lined with a synovial membrane 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Suture Syndesmosis gomphosis Mobility 1. 3. Immobile (synarthrosis) Slightly moveable (amphiarthrosis) Immobile Synchondrosis (hyaline) Symphysis (fibrocartliage) 1. 2. Immobile Slightly moveable Plane Hinge Pivot Condyloid Saddle Ball and socket Freely moveable (diarthrosis) which depends on joint design 2.