Functions
advertisement

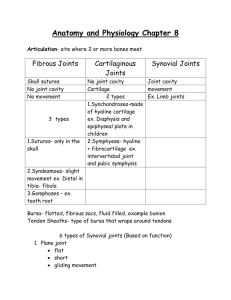
Types of Joints Definition: The site where two or more bones meet. Immovable - Fibrous joints • skull • tibia/fibula Types of Joints Immovable - Cartilaginous joints • Rib cage • Intervertebral discs Types of Joints Movable - Synovial Joints • Most joints in the body, including all joints of the limbs Characteristics: • Articular cartilage • Joint cavity/capsule • Synovial fluid • Ligaments • Tendons Joint Tissues Cartilage 1. Three Types • Hyaline • Elastic • Fibrocartilage 2. Functions • Provides support • Shock absorbance • Provides flexibility • Smooth movement Joint Tissues Cartilage Tissue Types – Hyaline Cartilage Functions Provides soft and smooth covering to end of bone (articular surface) Helps provide smooth and easy movement between bones (at joints) Provides the starting material for new bone growth Structure Matrix is spongy (like jello) and evenly distributed between the cells Cells (chrondocytes) are found in pairs within capsules called lacunae Hyaline Cartilage Tissue Types - Fibrocartilage Functions Shock absorber for structures subjected to pressure (meniscus, intervertebral discs) Structure Tough tissue with matrix of many collagenous fibers Fibrocartilage Joint Tissues Ligaments and Tendons – Dense Connective Tissue Tissue Types Dense Connective Tissue Functions Ligament- bone to bone connection, stops abnormal movement Tendon – bone to muscle connection, creates normal movement Structure Tough tissue with matrix of many collagenous fibers and a fine network of elastic fibers Dense Connective Tissue Joints Anatomy and Physiology Lab Fetal Pig Joint