Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 8
advertisement
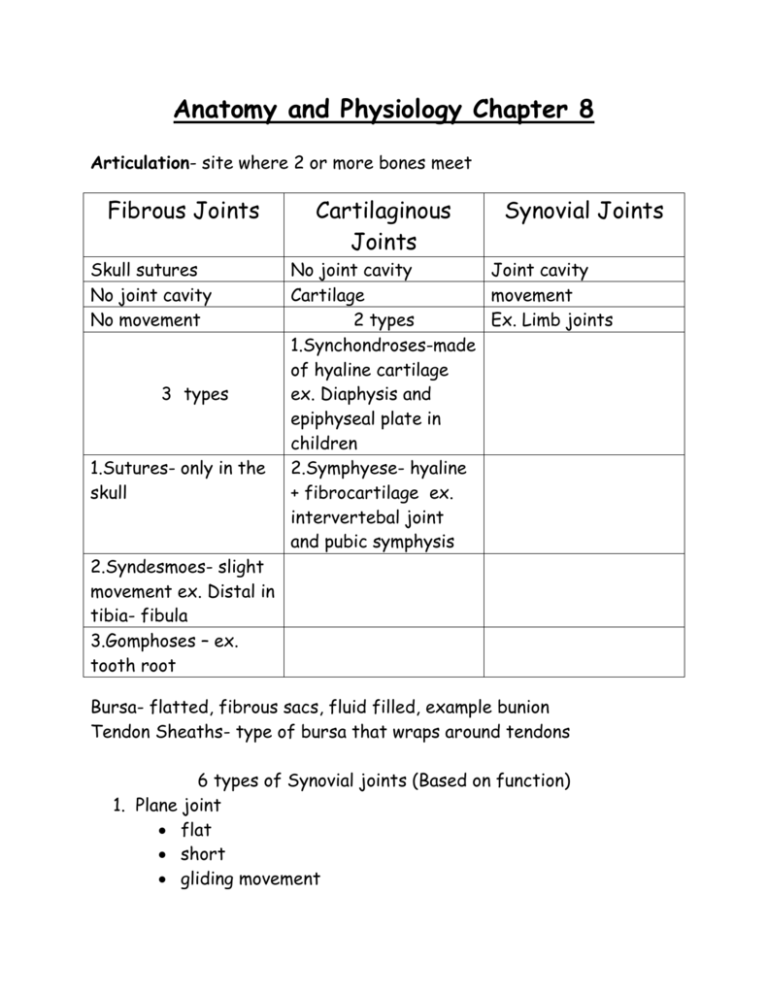
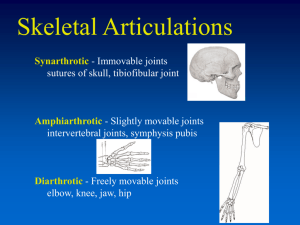
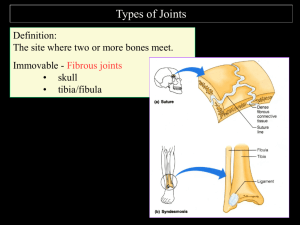
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 8 Articulation- site where 2 or more bones meet Fibrous Joints Skull sutures No joint cavity No movement 3 types 1.Sutures- only in the skull Cartilaginous Joints Synovial Joints No joint cavity Joint cavity Cartilage movement 2 types Ex. Limb joints 1.Synchondroses-made of hyaline cartilage ex. Diaphysis and epiphyseal plate in children 2.Symphyese- hyaline + fibrocartilage ex. intervertebal joint and pubic symphysis 2.Syndesmoes- slight movement ex. Distal in tibia- fibula 3.Gomphoses – ex. tooth root Bursa- flatted, fibrous sacs, fluid filled, example bunion Tendon Sheaths- type of bursa that wraps around tendons 6 types of Synovial joints (Based on function) 1. Plane joint flat short gliding movement 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Example vertebrae articular processes intercarpal and intersal joint Hinge joint Uniaxial hinge Example elbow and interphalangeal joint( fingers and toes) Pivot joints Rounded bone fits into a ring of bone(or tendons) Uniaxial rotation Example “shake head no” rotaion of head radius within ring of tendon of ulna Condyliod joint One bone fits into depression of another * both surfaces are oval* Example wrist and knuckle Saddle joint Each bone surface has both concave/convex Forms saddle Example thumb Ball and Socket joint Shpherical had articulates with cup shape of another The most free moving joint Example hip joint and shoulder bone Shoulder (Glenohumeral) Joint Ball and socket joint Humerus head fits into the glenoid cavity (shallow) of scapula 4 total ligaments: 1 coracohumeral ligament + 3 glenohumeral ligaments = rotator cuff Knee Joint Largest and most complex joint in body Extension, flexion and some rotation Actually 3 joints in one 3 ligaments o Extracapsular Fibular and tibial collateral ligaments o Oblique popliteal ligament o Arcuate politeal ligament o Intracapular ligament are called cruciate ligaments- they form a cross with each other forming an X (Cruci= cross) The ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) Elbow Flexion and extension only Radius and ulna articulate with the condyles of the humerus Radius is an “onlooker” in the angular elbow movement Common Joint injuries Sprains- torn or stretched ligaments , common areas are lumbar, ankle, and knee Cartilage injury- more common, cartilage fragments can be removed arthroscopically Dislocation- often repeated injury Common types of arthritis: Acute form often caused by bacterial infection Chronic types: Osteoarthritis- OA , 85% of all Americans will get this, more cartilage destroyed than replaced, bony spurs form, treated with glucosamine sulfate and pain relievers Rheumatoid Arthritis- 40-50 year old, X3 women than men, 1% Americans, RA, autoimmune disorder Gouty Arthritis- “gout” Uric acid settles in soft tissues and joint, more common in males, avoid liver, kidney, and sardines, excess alcohol