Use old plasmid maps and gel electrophoresis examples to analyze
advertisement

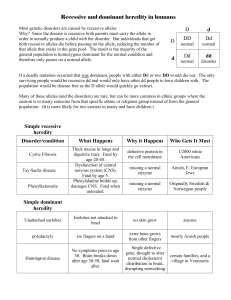
• Take your review sheet and notes, and check if you have all necessary notes collected together. • If any notes are missing, use the on-line PPT’s, text book, other students’ notes to get missing notes. • Look over the review topics and notes and check which topics are the least familiar and most troublesome for you. • Get together with a group that is reviewing THE SAME TOPICS THAT YOU NEED TO MOST REVIEW ON • Explain topics to each other and quiz each other • Answer review questions on ALL REVIEW TOPICS • State the central dogma of biology • Define transcription, name its location and its steps. • Define translation, name its location and its steps. • Differentiate passing on genetic information in eukaryotes and prokaryotes. • List and briefly describe the steps of transcription • How many nucleotides are needed to determine an amino acid? On what molecule do you find the nucleotides that directly determine an amino acid? • List and describe the steps of mRNA modification. • In what organisms does mRNA modification occur? • Define and state the location of translation. • What is the main purpose of translation? • List and briefly describe the steps of translation. • What type of gene mutation would cause the – Largest change in a new protein? – The least change in a new protein? • Where does the termination of transcription occur? • If the DNA sequence is the following below, what is the RNA and amino acid sequence that is coded by it? 3’ATTCGGTAGCCATAA5’ • Define mutation and differentiate between its two forms. • State the law of segregation. • Differentiate between codominance and incomplete dominance. • Name two evidence of evolution and explain how they provide proof of evolution. • Cystic fibrosis is carried on the recessive allele. Normal is dominant. A normal man and a woman with cystic fibrosis have one CF child and one normal child. What are the chances that their next child will have cystic fibrosis? • In peas, tall is dominant to short. If a pure tall and a pure short plant are crossed, and the resulting offspring are crossed, how many of the F2 will be short if 120 plants are produced? • In guinea pigs, black is dominant to white. If two black guinea pigs are crossed and 4 black and 3 white pigs result, were the parents pure? • In 4 o'clock flowers, red is dominant to white, but the heterozygote is pink. What is the phenotype ratio of crossing red 4 o’clock flowers and pink 4o’clock flowers? • If Jennifer is normal (and is not a carrier) but her husband, James, is colorblind, what are the chances of A. their daughter, Jean, being colorblind? B. Of their son, Joe being colorblind? • List the three types of natural selection and provide an example of each. • Describe how DNA can be used as evidence of evolution. • In a population, 4 % of all individuals show the recessive trait. What is the allele frequency of the dominant allele? What is the frequency of the heterozygous individuals? • In a population, 560 out of 1000 individuals show the dominant trait. What is the frequency of the recessive allele? Dominant allele? What is the frequency of the homozygous dominant individuals? • In a population of butterflies, the dark coloration is dominant over the light coloration. What is the frequency of the recessive allele if 23 out of 67 butterflies are light? • List 4 mechanisms of evolution and explain how they change the genetic makeup of the population. • Describe how Darwin contributed to the theory of evolution. • Give 4 examples of evolution and explain two of those. • Use examples to differentiate between directional and stabilizing selection. • List the aspects of natural selection in order. • Differentiate between DNA and RNA. • List the different types of RNA molecules and describe their function. • Name an enzyme that participate in transcription. Describe its function. • Describe the structure of a ribosome and its function. • Why is colorblindness more common in men than in women? • Name an example of a vestigial structure. Why do vestigial structures provide evidence of evolution? • What are restriction enzymes? How are they used by scientists? • What is PCR? What is it used for? • Name three advantages and two disadvantages of using biotechnology. • Describe what gel electrophoresis is and how it benefits scientists. • What is DNA sequencing? How is it beneficial for science? • What are GMO’s? How can they be useful? Harmful? Use old plasmid maps and gel electrophoresis examples to analyze those. • Describe the main purpose of cellular respiration and the organisms that perform it. • List the steps of cellular respiration and their locations. • Describe the location, reactants, products and main purpose of glycolysis. • Describe the process of fermentation and the conditions when it takes place. • Explain how hydrogen ion concentration gradient is used to form ATP. • Describe what processes of CR or PS produce the following: – CO2 – NADPH – NADP+ – FADH2 – NAD+ – H2O – O2 – ATP • List the steps and locations of photosynthesis. • Name the main purpose of photosynthesis and the organisms that perform it. • Draw the parts of the leaf and describe how each part contributes to photosynthesis. • What is the role of guard cells? • What are the reactants and products of the light reaction? • Draw the process of the light reaction and describe its steps. • Draw the process of the Calvin cycle and describe its steps. • State Mendel’s independent assortment and law of dominance. • List three factors that would influence the rate of photosynthesis and describe how these factors would influence photosynthesis.