Recessive and dominant heredity in humans
Recessive and dominant heredity in humans
Most genetic disorders are caused by recessive alleles
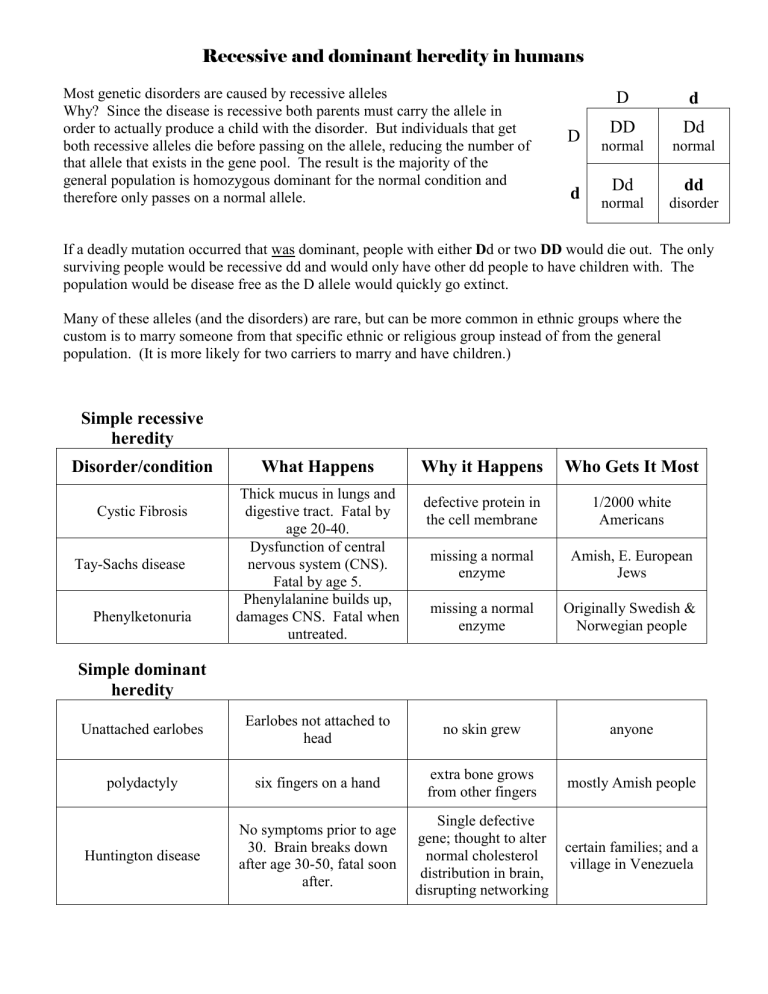
Why? Since the disease is recessive both parents must carry the allele in order to actually produce a child with the disorder. But individuals that get both recessive alleles die before passing on the allele, reducing the number of that allele that exists in the gene pool. The result is the majority of the
D
D
DD normal
d
Dd normal general population is homozygous dominant for the normal condition and therefore only passes on a normal allele.
d
Dd normal
dd
disorder
If a deadly mutation occurred that was dominant, people with either D d or two DD would die out. The only surviving people would be recessive dd and would only have other dd people to have children with. The population would be disease free as the D allele would quickly go extinct.
Many of these alleles (and the disorders) are rare, but can be more common in ethnic groups where the custom is to marry someone from that specific ethnic or religious group instead of from the general population. (It is more likely for two carriers to marry and have children.)
Simple recessive heredity
Disorder/condition Why it Happens Who Gets It Most
Cystic Fibrosis
Tay-Sachs disease
Phenylketonuria
What Happens
Thick mucus in lungs and digestive tract. Fatal by age 20-40.
Dysfunction of central nervous system (CNS).
Fatal by age 5.
Phenylalanine builds up, damages CNS. Fatal when untreated. defective protein in the cell membrane missing a normal enzyme missing a normal enzyme
1/2000 white
Americans
Amish, E. European
Jews
Originally Swedish &
Norwegian people
Simple dominant heredity
Unattached earlobes
Earlobes not attached to head no skin grew anyone polydactyly
Huntington disease six fingers on a hand extra bone grows from other fingers mostly Amish people
No symptoms prior to age
30. Brain breaks down after age 30-50, fatal soon after.
Single defective gene; thought to alter normal cholesterol distribution in brain, disrupting networking certain families; and a village in Venezuela











