Notes Chapter 5
advertisement

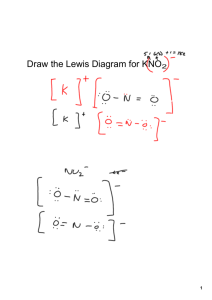
Nomenclature Naming Compounds Binary Compounds - composed of two elements 1. Contain a metal and a nonmetal 2. Contain two nonmetals Binary Ionic Compounds - cation (metal ion) - anion (nonmetal ion) Type I - metal forms only one ion (Table 5.1 p. 125) 1. Cation first, anion second 2. Cation - name the element 3. Anion - change end of element name to -ide Examples - NaCl Na+ sodium chloride Cl- - MgO Mg2+ O2magnesium oxide - CaS Ca2+ S2calcium sulfide Type 2 - metal forms more than one cation (Table 5.2 p. 128) 1. Cation first, anion second 2. Cation charge is specified by a Roman numeral in parentheses Examples - CuCl Cu?+ Clcopper(I) chloride Fe?+ O20 = 2(?) - 3(2-) 6 = 2(?) 3=? iron(III) oxide - PbCl4 Pb?+ Cl0 = ? + 4(-1) 4=? lead(IV) chloride -Fe2O3 Strategy for binary compounds Decide if the cation has only one charge or can have multiple charges If cation has one charge, name both ions b. If cation can have multiple charges, use Roman numeral in parentheses to show the charge a. Type III - contains only nonmetals 1. First element in formula is named first using full element name. 2. Second element is named as though it were an anion (-ide ending). 3. Prefixes are used to denote the number of atoms present (Table 5.3 p. 132) 4. Never use mono for naming first element. Examples BF3 boron trifluoride NO nitrogen monoxide N 2O 5 dinitrogen pentoxide Polyatomic ions - ion composed of several atoms, but are bound together so they act as one unit - Table 5.4 p. 137 -oxyanion - series of polyatomic ions that contain an atom of a given element and different numbers of oxygen atoms ClOhypochlorite ClO2chlorite ClO3chlorate ClO4perchlorate Examples Na2SO4 sodium sulfate KH2PO4 potassium dihydrogen phosphate Mn(OH)2 manganese hydroxide NH4ClO3 ammonium chlorate Naming Acids Compounds that produce H+ ions when dissolved in water 1. If anion does NOT contain oxygen *prefix hydro-, suffix -ic acid Examples H2S - hydrosulfuric acid HCl - hydrochloric acid 2. If anion contains oxygen root name of central atom *anion ends with ate - suffix -ic acid Example H2SO4 - sulfate ion - sulfuric acid *anion ends with ite - suffix -ous acid Example HNO2 - nitrite ion - nitrous acid Writing formulas from names Use names of elements to write the formula. You must check the charges of the ions (including polyatomic ions) to make sure the net charge on the compound is zero. Examples calcium chloride Ca2+ Cl- ---> CaCl2 dinitrogen pentoxide N 2O 5 sodium carbonate Na+ CO32- ---> Na2CO3 nitric acid nitrate NO3- ---> HNO3 lead(IV) oxide Pb4+ O2- ---> PbO2