Nomenclature - Cloudfront.net
advertisement

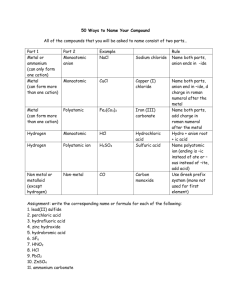
Nomenclature Chapter 9 Types of Ions Monatomic – contains only one atom Examples: Na+, FCharge is equal to oxidation number, which is the number of electrons transferred. Polyatomic – contains more than one atom Examples: NH4+, OHIf the anions contain at least one oxygen then they are called oxyanions. Oxyanions In general there are two types of oxyanions formed about the same second atom. The ion with one more oxygen is always named with the suffix –ate. Sulfate – SO42The ion with one less oxygen is always named with the suffix –ite. Sulfite – SO32- Chemical Formula When writing a chemical formula for an ionic compound, one always writes the chemical symbol for the cation first and the chemical symbol for the anion second. You place a subscript number to the lower right to represent the number of each ion in the formula. Al2O3 For only one ion you place no number. NaCl Types of Compounds to Name 1. Type I – Ionic compound from the representative elements (only A groups) - (Metal-Nonmetal) 2. Type II – Ionic compound where the cation is a transition metal (d-block) - (Metal-Nonmetal) Exceptions: Ag+, Zn2+, Cd2+ (Type I) Pb and Sn (Type II) 3. Type III – Molecular compound (all Nonmetals) 4. Type IV – Acids (Formula begins with H, Name ends with Acid) Type I Naming Binary: Write the name of the metal cation followed by the changed suffix of the anion to –ide. Example: NaCl – Sodium Chloride Ternary: Write the name of the metal/polyatomic cation followed by the name of the element/polyatomic anion from the back of the periodic table. Example: Mg(OH)2 – Magnesium Hydroxide Type I Formulas Binary: Find the two elements named and identify their charges. If equal, write the two element symbols cationanion. Calcium Oxide - CaO If unequal, write the symbols and swap the charges to subscripts leaving out any 1s. Aluminum Fluoride – AlF3 Type I Formulas Ternary: Find the metal/polyatomic cation and the element/polyatomic anion and identify their charges. If equal write the symbols cation-anion. Potassium Nitrate - KNO3 If unequal write the symbols and swap the charges to subscripts leaving out any 1s and placing parentheses around any polyatomic with a subscript >1. Barium Cyanide – Ba(CN)2 Type II Naming Both Binary and Ternary: Transition Metal Cation Look up anion and charge then calculate charge of transition metal. Cation = Anion Write transition metal name followed by the charge in parentheses as a roman numeral and then the name of the anion. NiBr2 – Nickel (II) Bromide FePO4 – Iron (III) Phosphate Type II Formulas Both Binary and Ternary: Transition Metal Cation The roman numeral is the charge of the transition metal cation, look up the anion charge If equal write the symbols cation-anion. Copper (I) Fluoride – CuF If unequal write the symbols and swap the charges to subscripts leaving out any 1s and placing parentheses around any polyatomic with a subscript >1. Gold (II) Nitrite – Au(NO2)2 Type III Naming Uses prefixes to tell you how many of each element are in the compound. The prefixes are Mono, Di, Tri, Tetra, Penta, Hexa, Hepta, Octa, Nona, and Deca. Write the first element like you would a metal in Type I including any prefix other than Mono. Then write the second element the same way you would in Type I including any prefix. CO2 – Carbon Dioxide N2O – Dinitrogen Monoxide SF6 – Sulfur Hexafluoride Type III Formulas From the prefixes write the elements with their appropriate subscripts. Carbon Monoxide - CO Dinitrogen Pentaoxide – N2O5 Phosphorous Trichloride – PCl3 Type IV Naming Binary Acids – Contain no Oxygen Start with HydroChange the anion suffix to –ic Add the word Acid HBr is Hydrobromic Acid HCN is Hydrocyanic Acid Exceptions: NH3 is Ammonia and H2O is Water Type IV Naming Ternary/Oxy acids: Contain Oxygen Start with the name of the base anion, but change the –ate suffix to –ic, add Acid or change the –ite suffix to –ous, add Acid HNO3 – Nitric Acid H2SO3 – Sulfurous Acid Type IV Formulas Binary Acids – Contain no Oxygen Find the symbol and the charge for the anion, add Hydrogens to equal the charge. Hydrosulfuric Acid - S2- - H2S Ternary Acids – Contains Oxygen Find the polyatomic anion and its charge, add Hydrogens to equal the charge.