Chemical Names and Formulas
advertisement

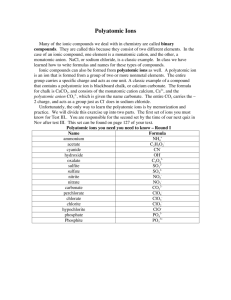
Chapter 9 Essential Questions How does the periodic table help you determine the names and formulas of ion and compounds? What is the difference between an ionic and molecular formula? How do we determine the charges of monatomic ions? Monotomic ions are the simplest ions They either cations or anions Positive, metals, give away electrons to obtain the configuration of a noble gas state. Negative, nonmetals, take electrons to obtain the configuration of a noble gas. Naming Monotomic Ions Metals are named using the name of the metal Sodium ion, calcium ion, aluminum ion Anions Start with the stem of the element and end in ide Oxide, Sulfide, Nitride Naming Monotomic Ions Some metals form more than one ion Transition metals 1B-8B Two ways used to name these metals Stock method Fe2+ Iron(II) Fe3+ Iron(III) Naming Monotomic Ions Classical System The classical name of the element is used to form the root Ferrous ion, Ferric ion List the symbols and names of common metal ions with more than one charge. Make flash cards for memorization (HW) Practice Write the symbol, including the charge for the ion formed by each element; classify each as anion or cation; then write the name of each ion. Arsenic Beryllium Fluorine Gallium Sodium As3-; anion; arsenide ion Be2+; cation; beryllium ion F-; anion; fluoride ion Ga3+; cation; gallium Na+; cation sodium ion Polyatomic Ions polyatomic ions Naming Ionic Compounds Writing ionic formulas Writing the Formulas for Ionic Compounds Practice problem 9.2 pg 246 Naming Binary Ionic Compounds If you know the formula, you can write its name Place the cation name first and the anion name second For compounds with elements that form only one ion, it is straight forward as in NaBr For compounds with elements that form more than one ion, the name of the metal must be . SnF2, SnO2 Sample Problem 9.3 pg 249 Practice Write the names of these binary compounds Li2O MgS MnCl3 FeO CaI2 Lithium oxide Magnesium sulfide Manganese(III) chloride Iron(II) oxide Calcium iodide Compounds with Polyatomic Ions The procedure is similar to binary compounds Write the symbol (or formula) for the cation Write the symbol (or formula) for the anion Add subscripts as needed to balance the charges Use which ever method you are comfortable with Use parenthesis when more than one polyatomic ion is necessary to balance charges Sample problem 9.4 pg 251 Naming Compounds with Polyatomic Ions First write the cation name If the cation has than one charge, use a roman numeral in the cation name Identify the polyatomic ions and write that in the name Sample problem 9.5 pg 253 Practice Name the following compounds Na2CO3 Pb(OH)2 FeN NH4NO3 Mg(NO3)2 Naming and Writing Formulas for Molecular Compounds Write the of the elements in the order listed in the formula Use prefixes to indicate the number of each kind of atom. You do not have to use mono. The vowel at the end of a prefix is dropped if the element begins with a vowel End the name with the suffix ide Memorize the chart of prefixes on page 257 Practice problems 9.6 pg 258 Naming and Writing Formulas for Molecular Compounds Writing formulas for Binary Molecular Compounds Use the prefixes to determine the subscript Write the correct symbols for each element with the appropriate subscripts Naming and writing formulas for acids and bases Naming Acids The general formula for an acid is HnX n is the number of hydrogen ions combined with the anion The naming depends on the anion (X) If the anion ends in ide, the prefix is hydro, the anion has the suffix ic hydrochloric acid If the anion ends in ite, the stem ends in ous sulfuous acid If the anion ends in ate, the stem ends in ic nitric acid Chart pg 260