Chapter 17 Carbonyl Compounds II 17.4
advertisement

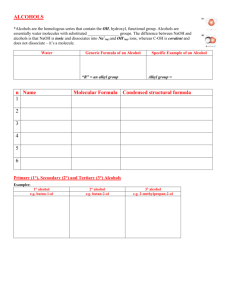
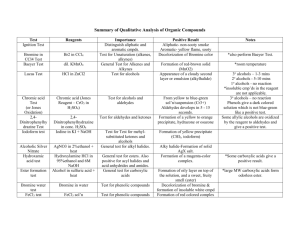
Main Menu 17.4 How Aldehydes and Ketones React (Part III) d- Electron rich (Lewis base, Nu) d+ Electron deficient (Lewis acid, E+) R = alkyl or aryl (C) Y = alkyl, aryl or H (class II) (No leaving group) 1 Nucleophilic Addition (Class II) 1. General mechanism in basic condition: 2. General mechanism in acidic condition: 2 Important pKa to Remember Acids H-Z Names Alkane (2°) Amine H3C CH H H3C H N H H Hydrogen Thiol 51 38 Conjugate Base, :Z H3C CH H3C H N H H 35 H Base as Li+ salt Nucleophile as Grignard reagent Base and Nucleophile R NH H H S Carboxylic Acid RCO 2 Hydrochloric Acid Cl 10-11 H 10-11 H 4-5 H -7 Base in NaH, CaH2 Nucleophile in LiAlH4, NaBH4 Often as a base but can be a nucleophile 15-16 R General Roles of :Z H Alcohol water Ammonium Approx. pKa R NH H R S RCO 2 Cl Weak base, but can be a nucleophile Nucleophile Weak base, poor leaving group Leaving group, poor nucleophile 3 Types of Nucleophile for Class II Carbonyl Groups 1. Carbon as the nucleophilic atom Basic condition pKa = 25 pKa = 50 carboanion Acetylide ion 2. Hydrogen as the nucleophilic atom hydride Mostly basic condition 3. Nitrogen as the nucleophilic atom 1° and 2° amines Mostly acidic condition 4. Oxygen as the nucleophilic atom 1° alcohols Acidic condition 4 Oxygen as the Nucleophilic Atom pKa of alcohol. pKa = -2 pKa = 15-16 1° and 2° Alcohols function as weak acids, weak bases or nucleophiles. 3° Alcohols function as weak acids or weak bases. 5 Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones with Alcohols General reaction with primary alcohols: 2° and 3° Alcohols are too hindered to react. H+ 2 1° Alcohols Ketal or acetal General reaction with water: H+ Geminal diol (gem-diol) 6 Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones with Water Example: H+ Mechanism: 7 Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones with Alcohols Examples: 2 2 1 H+ H+ H+ 8 Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones with Alcohols Mechanism: hemiacetal acetal 9 Application of Ketal or Acetal Synthesis using protecting group ? LiAlH4 or DIBAL will reduce the ketone as well. Ketal as the protecting group for ketone: Ketals like ethers are relatively stable in basic condition. 10 Mechanism for the Formation of Cyclic Ketal 11 More Examples on the Use of Protecting Groups ? SOCl2 (PBr3 or PCl3) will convert carboxylic acids into acyl halides as well. Ester as the protecting group for carboxylic acid: Ester will not react with SOCl2 (from compound 3 to compound 4). 12 More Examples on the Use of Protecting Groups NH2 NH2 ? Amines under acidic condition may turn into an EWG in the form of ammoniim ions. NO2 Amide as the protecting group for amine: Amide in compound 3 will act as EGD.. 13 Formation of Cyclic Hemiacetals or Ketals Intramolecular reaction: formation of 5 or 6-membered rings 14 Cyclic Hemiacetals in Carbohydrates Intramolecular formation of 5 or 6-membered rings 1 CHO 2 H OH 3 HO D-Glucose H 5-OH 5 5 O HO HO 4 H OH OH 1 OH OH + O HO HO 1 OH OH OH 5 H OH 6 CH OH 2 1 CHO 2 H OH 3 HO H 4 H 4-OH OH 4 HO OH OH HO O 1 OH 5 H OH HO + 4 HO O 1 OH OH OH 6 CH OH 2 15 Learning Check 1. What could be the reagent and reaction condition for the following transformation? O (a) ethanol, NaOH H3CH2CO OCH2CH3 ? (b) ethanol, H+ CH3 CH3 (c) methanol, NaOH (d) methanol, H+ (e) None of the above 2. What should be the product from the following reaction? 16 Learning Check 3. What could be the product for the following reaction? OH O OH Product? H+ removal of water (a) (b) O O OH O O (c) O O OH (d) OH O O O (e) None of the above 17 Learning Check 4. Which hydroxy group when added to the aldehyde functional group (C-1) of open chain glucose will produce the cyclic hemiacetal form shown below? (a) The one that locates on C-2. (b) The one that locates on C-3. (c) The one that locates on C-4. (d) The one that locates on C-5. (e) None of the above 18 Learning Check Main Menu 5. Which hydroxy group when added to the aldehyde functional group (C-1) of open chain glucose will produce the cyclic hemiacetal form shown below? (a) The one that locates on C-2. (b) The one that locates on C-3. (c) The one that locates on C-4. (d) The one that locates on C-5. (e) None of the above 19