Naming Compounds Containing Polyatomic Ions
advertisement

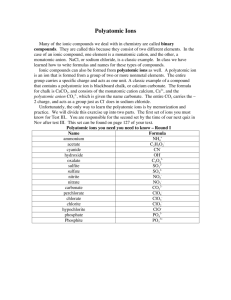
Salts Containing Polyatomic Ions Acids Oxyacids HW: Read 4-4 &4-6 Do problems 32, 34, 47, & 48 on pgs 133-134 Polyatomic Ions are groups of more than one atom that are bonded covalently, and have a net charge. There are several polyatomic ions that whose names and formulas MUST be memorized. They are found on table 4-2 on page 122. This website may also be helpful… http://antoine.frostburg.edu/chem/senese/101/co mpounds/polyatomic.shtml Polyatomic ions are found in nonbinary ionic compounds, and in oxyacids. To name a polyatomic Ion in an ionic compound: • If the poly atomic ion is first, and the anion is monoatomic, name the polyatomic ion, then name the anion as usual, replacing its ending with the suffix –ide. • If the polyatomic ion is second, first name the cation as a type I or type II depending on what it is, including the roman numerals for type II, then name the polyatomic ion. • If both cation and anion are polyatomic, just name each polyatomic ion in the order in which they occur. Na2SO4 Sodium sulfate Fe(NO3)3 Iron Na2SO3 Sodium KH2PO4 Potassium (III) Nitrate Sulfite Dihydrogen Phosphate Mn(OH)2 Manganese (II) Hydroxide NH4ClO3 Ammonium Chlorate Ca(OH)2 Calcium Hydroxide Na3PO4 Sodium KMnO4 Potassium Phosphate Permanganate (NH4)2Cr2O7 Ammonium Co(ClO4)2 Cobalt KClO3 Potassium Cu(NO2)2 Copper Dichromate (II) Perchlorate Chlorate (II) Nitrate There are several definitions of acids. For now, an acid is a compound whose formula starts with hydrogen. There are two types of acids: 1. Regular Acids 2. Oxyacids Regular Acids are binary compounds containing hydrogen and one other nonmetal. The hydrogen will always come first. • Examples: HCl, H2S, H3N How do you tell how many H’s the acid of a nonmetal will have? • Balance the known charge of the nonmetal by adding Hydrogen (each H = 1+ charge). Naming Regular Acids 1. Use the prefix Hydro2. Use the nonmetal’s root 3. Use the suffix –ic 4. Finish with the word acid. Hydro-”root”-ic Acid • HCl = Hydrochloric Acid • H2S = Hydrosulfuric Acid • H3N = Hydronitric Acid HF Hydrofluoric Acid HI Hydroiodic HBr Hydrobromic H2O Hydroxic H2Se Hydroselenic Acid H3As Hydroarsenic Acid H3P Hydrophosphoric Acid Acid Acid Acid Oxyacids contain hydrogen, oxygen, plus one other nonmetal.. The hydrogen comes first. The oxygen and other element make up a polyatomic anion called an oxyanion. • Example: ClO4-, CO32-, NO3-, NO2-, etc… Remember you add the number of hydrogen atoms needed to balance the charge on the oxyanion. Oxyacids are named using the oxyanions from which they are made. If the oxyanion ends in –ate, then the suffix is changed to –ic, followed by the word acid. • HNO3 contains nitrate (NO3-): it is called nitric acid If the oxyanion ends in –ite, then the suffix is changed to –ous, followed by the word acid. • HNO2 contains nitrite (NO2-): it is called nitrous acid H2SO4 Sulfuric Acid H2SO3 Sulfurous H3PO4 Phorphoric H2CO3 Carbonic HClO Hypochlorous HC2H3O2 Acetic HCN Hydrocyanic Acid Acid Acid Acid Acid Acid