Honors Naming Acids Notes
advertisement

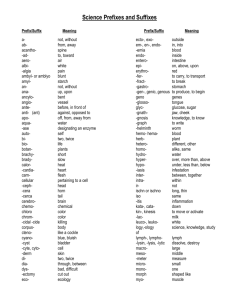
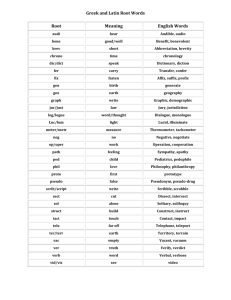
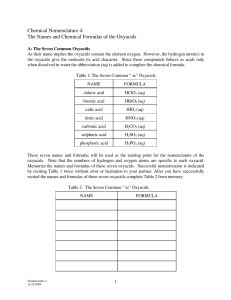
Naming Acids Haley Dana Chase Mykoal Nikki Maddie Brinda Oxyacids ● Any acid containing hydrogen and an oxyanion o oxyanion- a polyatomic ion containing oxygen Naming Oxyacids 1. 2. 3. 4. Identify the oxyanion Find the root of the oxyanion Change the suffix Add “acid” to the end -ate -ic -ite -ous Example: HNO3 1. Identify HNO3 as an Oxyacid 2. Identify the polyatomic a. Nitrate(NO3) 3. Change the suffix a. Nitrate→ Nitric 4. Add the word “acid” All together… Nitric Acid Example 2: Carbonic Acid 1. Identify Carbonic Acid as an oxyacid 2. Take off the word “acid” a. Carbonic 3. Change the suffix using the chart to identify the polyatomic acid a. Carbonic → Carbonate 4. Use the polyatomic formula a. CO3-2 5. Add Hydrogen to beginning a. -ic -ate -ous -ite H2CO3 6. Dont forget to swap and drop!!! Binary Acids ● Contains hydrogen and one other element Naming Binary Acids 1. Add prefix- Hydro 2. Find the root of the second element plus suffix -ic 3. Add “acid” at the end Example: HBr 1. HBr a. b. c. d. Add “Hydro” Root of bromine: Bromadd suffix: -ic Add acid at the end All together… Hydrobromic Acid Example 2 Hydrosulfuric Acid Strong Acid ● An acid that ionizes completely o ionizing: break apart into positive and negative ions ● Examples: o o o o o o Hydrochloric- HCl Hydrobromic- HBr Hydroiodic- HI Perchloric- HClO4 Nitric- HNO3 Sulfuric- H2SO4 The end